Making Skills Actionable at Scale
Transforming skill data into insights for employees and managers
Skills are the core currency of modern talent decisions from development and mobility to staffing and workforce planning.
But skills data only matters if people know what to do with it.
I led the design of the Skills experience across Career Hub, connecting assessments, gaps, and development actions into a single, actionable system.
As a result, even when skills data was available, users didn’t know what to do next. This wasn’t just a UX problem, it directly impacted:
customer adoption
manager effectiveness
and confidence in Eightfold’s AI-driven recommendations
-
-
Users
Employees, Managers, Org Leaders, AdminScope of Work
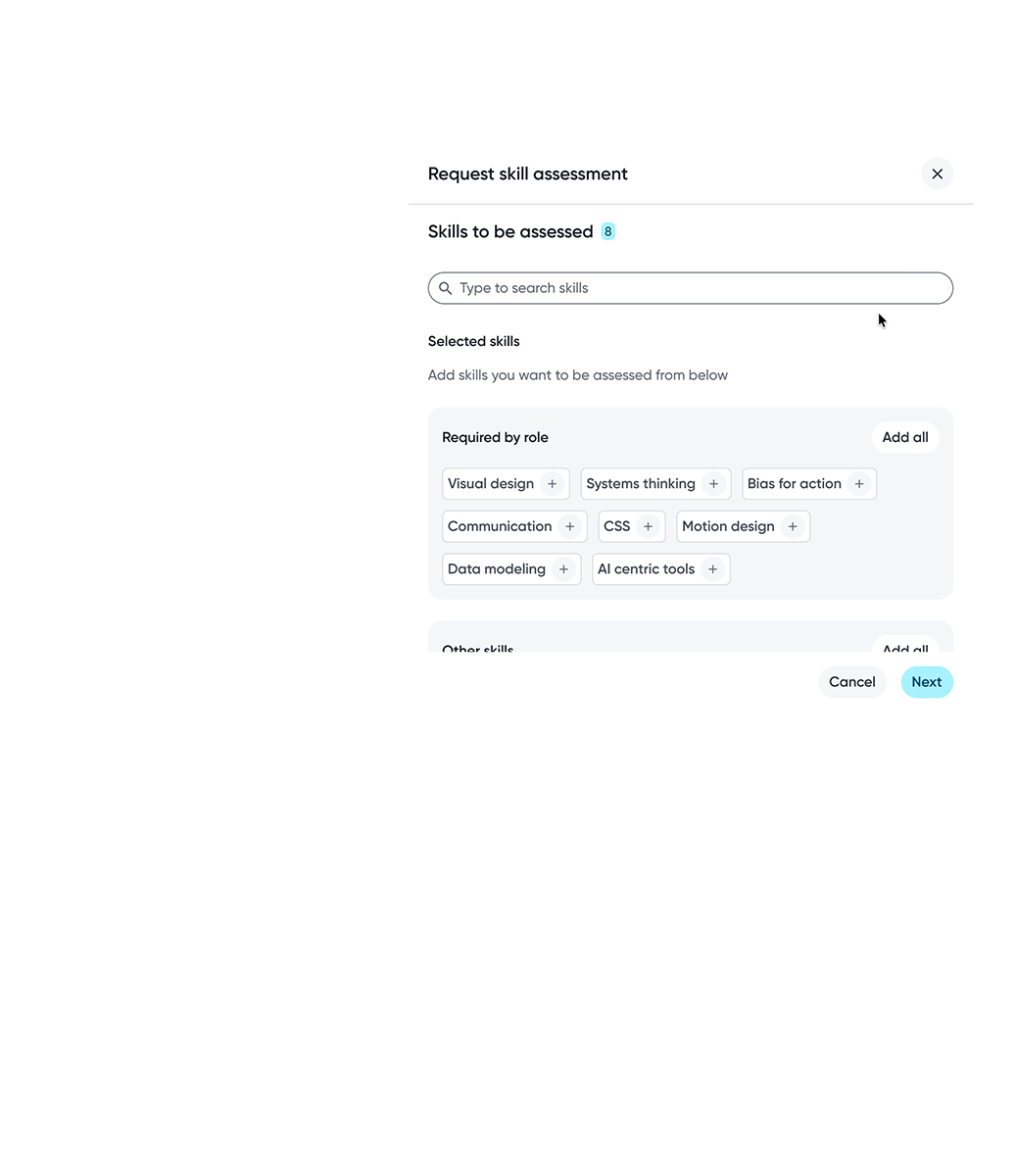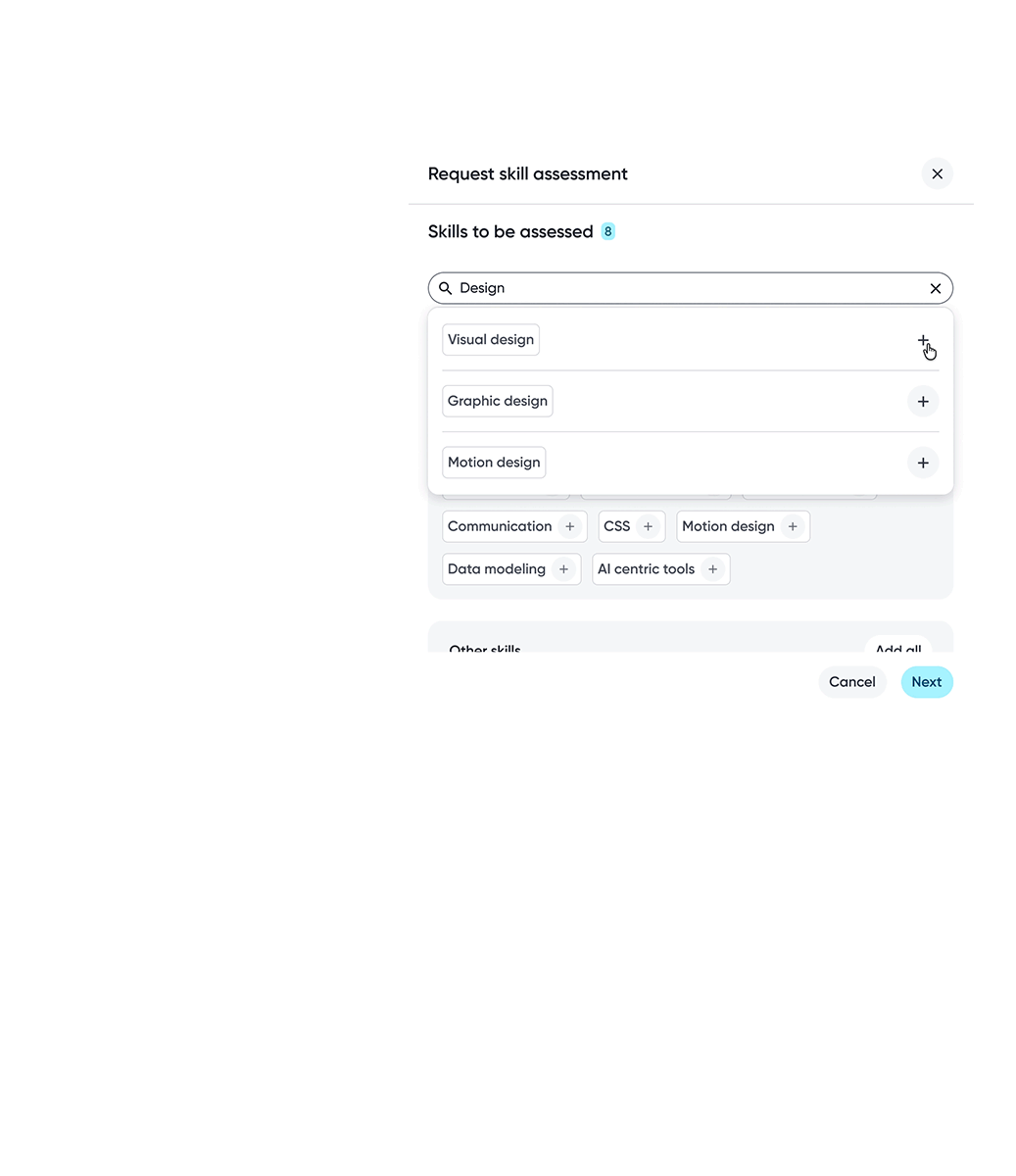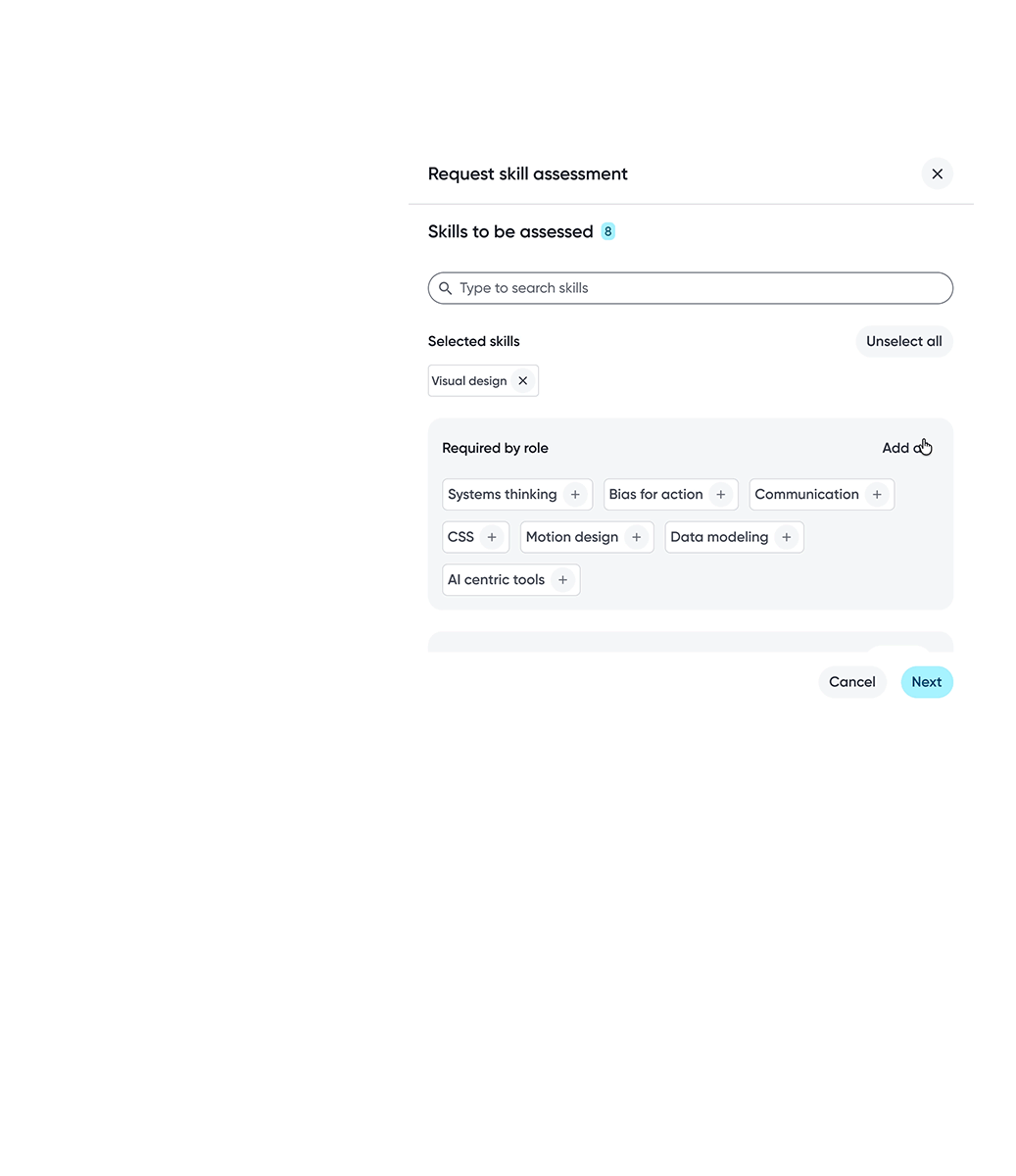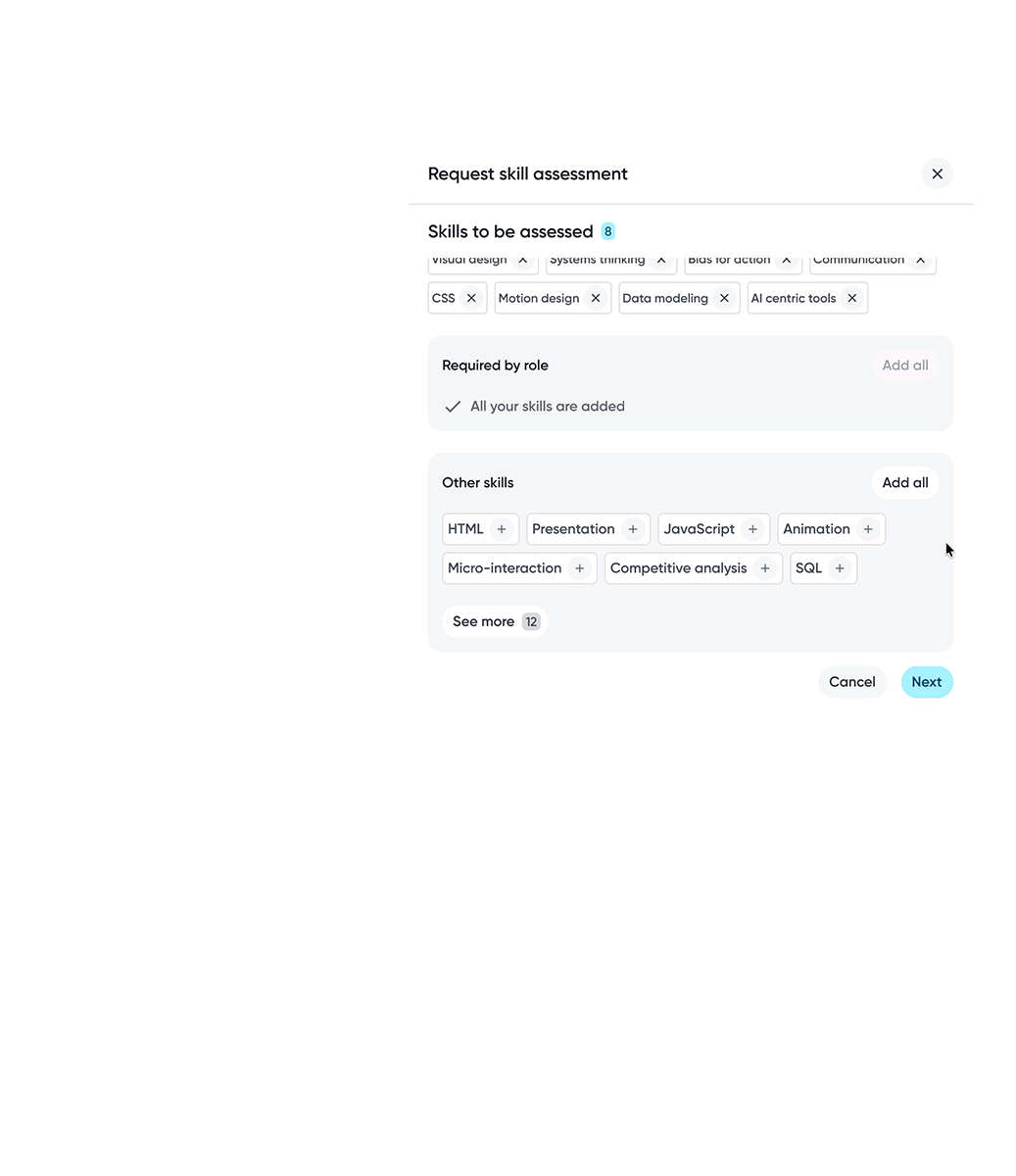
Skills Assessments
Skill Gap Identification
Development Plans
Manager Skill Insights
-
My Responsibilities
Experience strategy & systems design
End-to-end UX across multiple surfaces
AI-informed interaction design
Cross-functional collaboration (PM, Eng, UXR)
Design reviews & customer validation
Business Impact
Unblocked critical customer workflows (DTAG, Amdocs)
Enabled Early Availability rollout
Established foundation for scalable, skills-first talent insights
THE CORE ISSUE
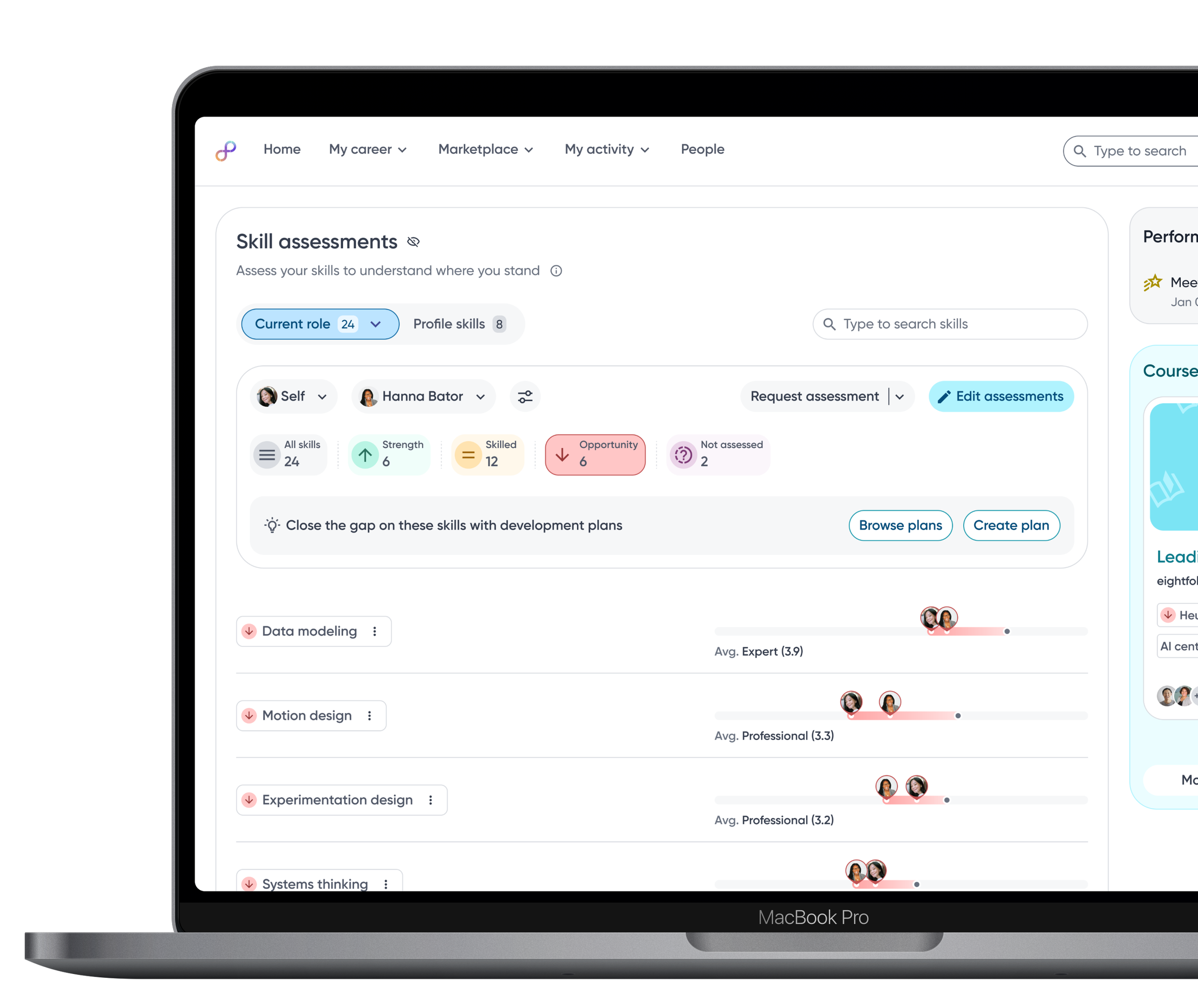
Assessments lived in dense, difficult to interpret tables
Managers lacked a scalable way to review team skills and gaps
Employees couldn’t easily understand what mattered and what to act on
Career Hub resources are disconnected from assessment insights

Research
LEARNING GOAL
We aimed to understand how skill data could meaningfully drive action across employees, managers, and teams.
RESEARCH INPUTS
-
In-depth customer conversations and early input partnership to understand real-world workflows, organizational constraints, and how skills were being used (or worked around) in practice.
-
Observed how users record, track, and interpreted skills data in current workflows.
Skill proficiency data is inconsistently captured and largely manual today. There is no clear feedback loop connecting insights to actions, or actions to measurable outcomes. -
Ran collaborative working sessions to align on technical constraints, map skill data flows across surfaces, and pressure-test assumptions across personas before moving into solution design.
I can see my skill gaps, but I’m not sure what I’m supposed to do with them.
JULIAN, EMPLOYEE
KEY INSIGHTS
Users don’t struggle with rating skills, they struggle with interpreting them. Numeric proficiency without context led to confusion and inaction.
Categories matter more than precision. Employees responded better to meaningful groupings of data than raw scores.
Skill gaps only matter if they lead somewhere. Surfacing gaps without pathways to action reduced trust in the system.
Managers need aggregation first, detail second. They want to know where to focus before diving into individual profiles.
STRATEGIC TAKEAWAY
Skill data existed, but it wasn’t designed to function as a decision-making system.
EMPLOYEE • SKILL ASSESSMENTS
Clear Skills. Clearer Growth Path.
Designing the employee experience to make skill proficiencies easy to understand and to empower meaningful action from skill gap awareness.
VISUALIZING
Making Skill Data Understandable at a Glance
To empower confident action, skill proficiency must be intuitively understandable. Making skill data understandable rethinks how skills are visualized, explored, and interpreted so users can quickly understand where they stand without decoding raw data.
Visualizing what matters
🔍 RESEARCH FINDING
Employees are overwhelmed with raw skill assessment data and they spend more time scanning and filtering than understanding.
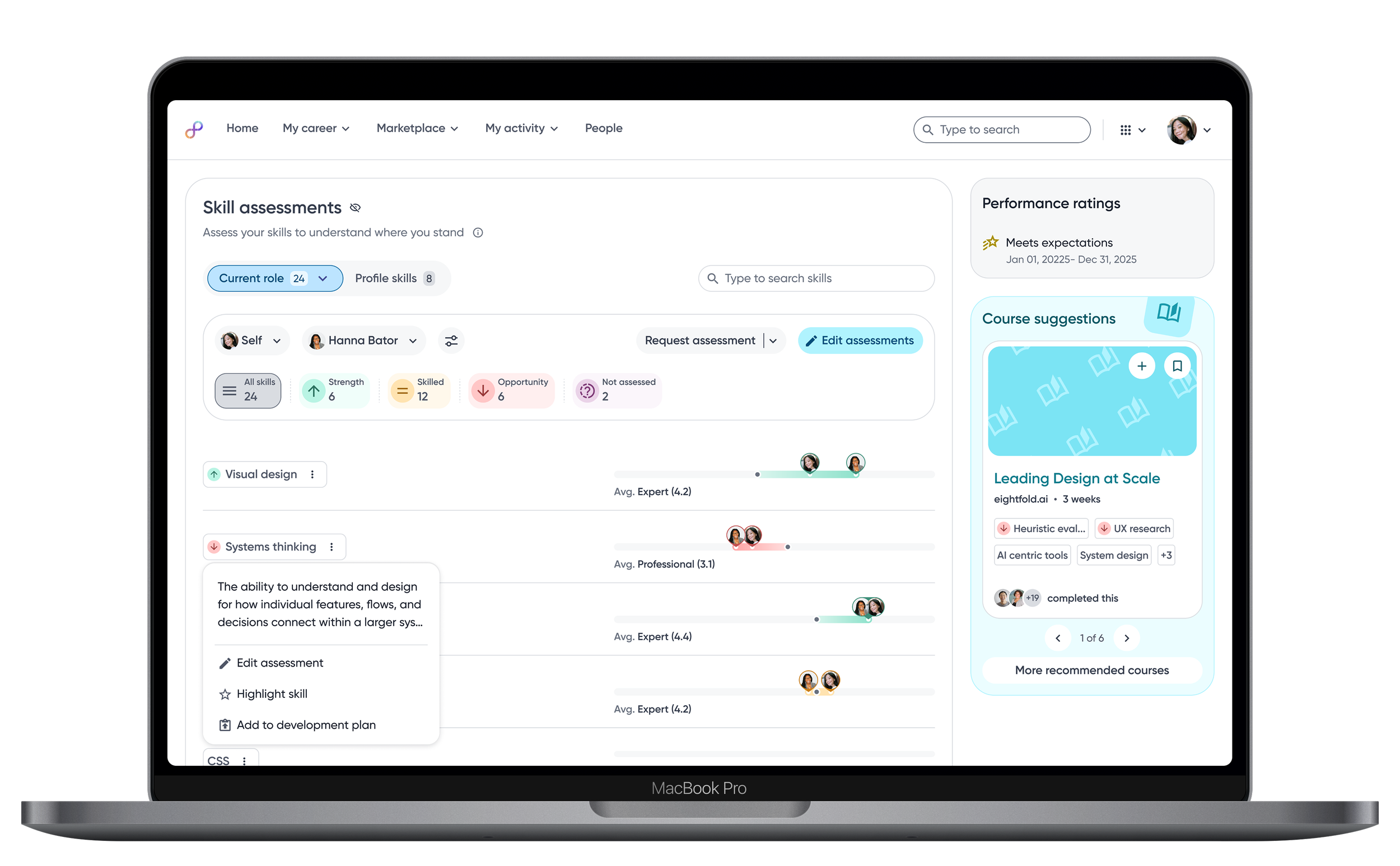
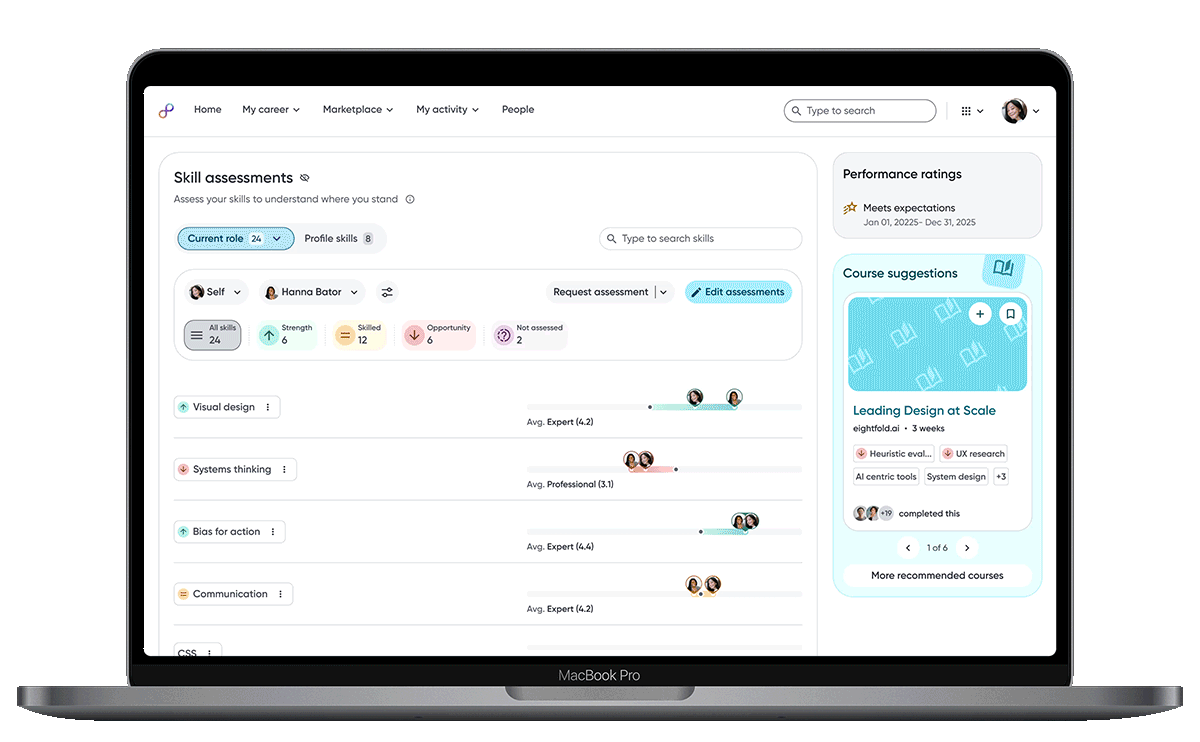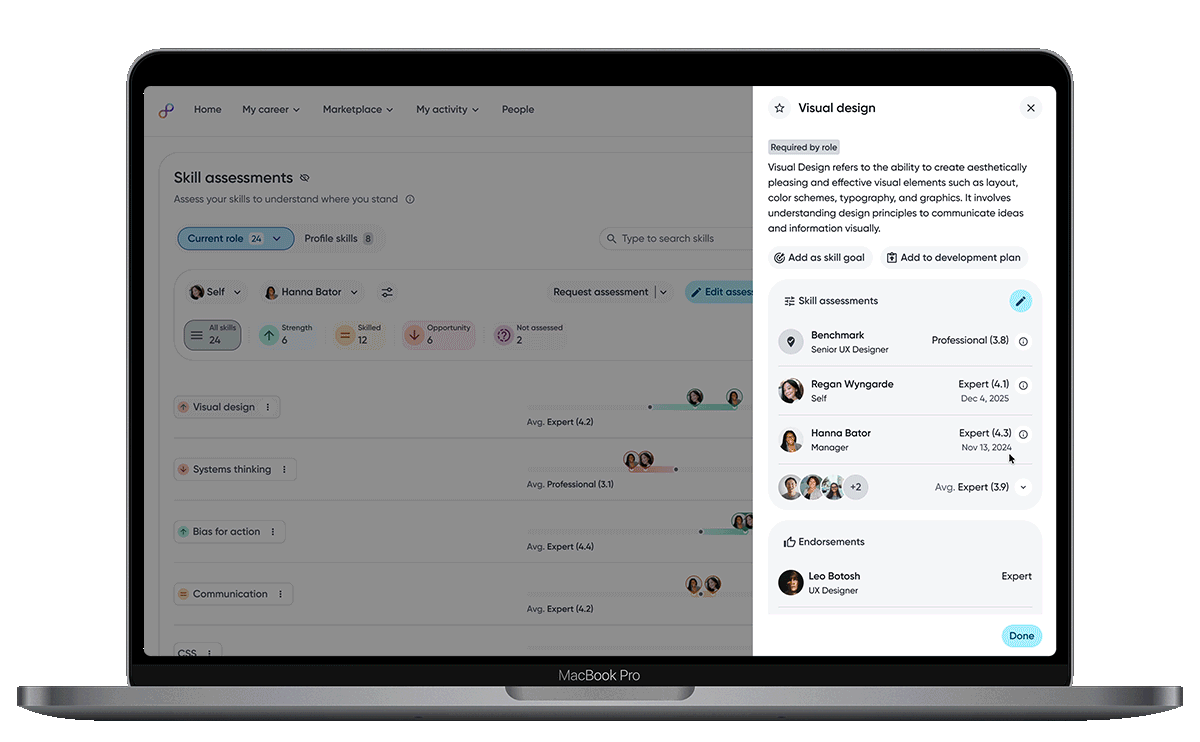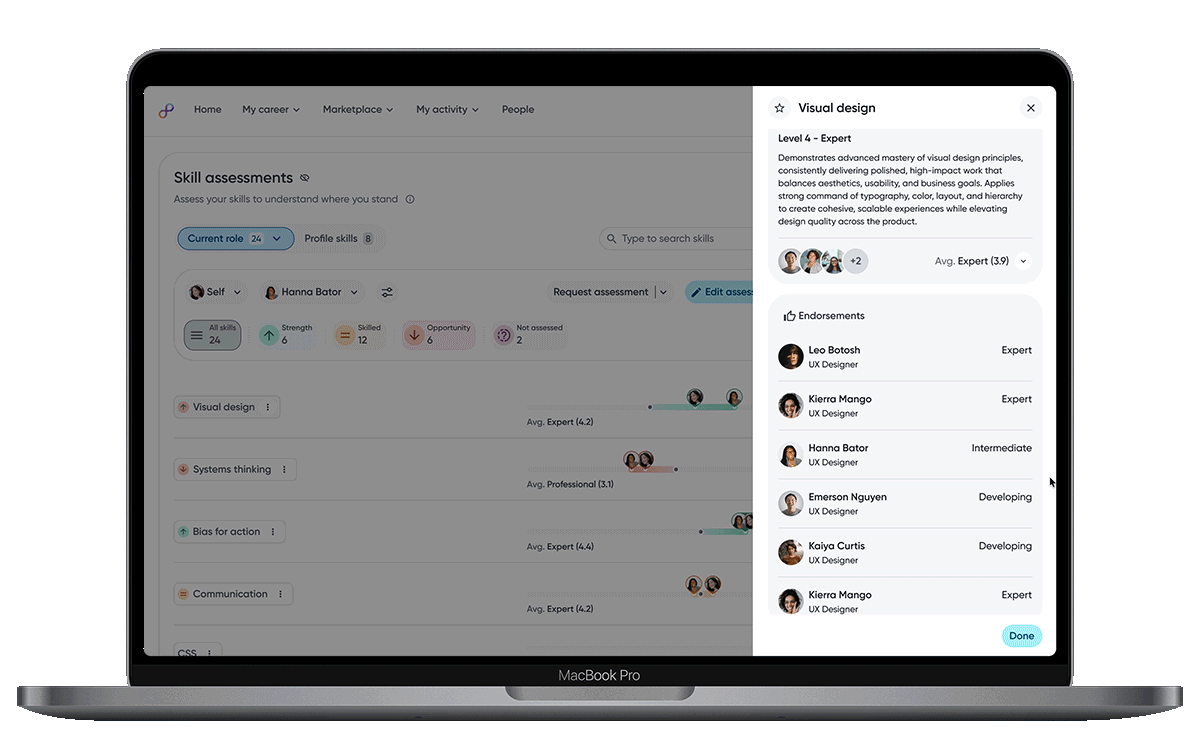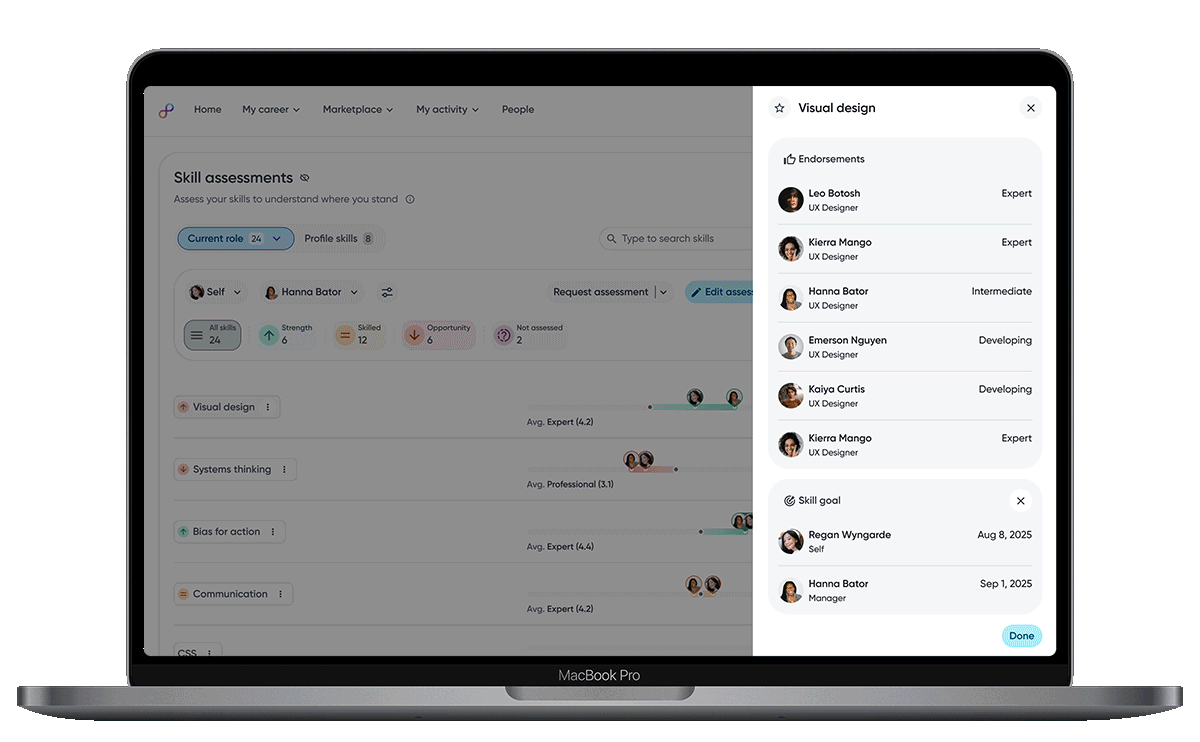
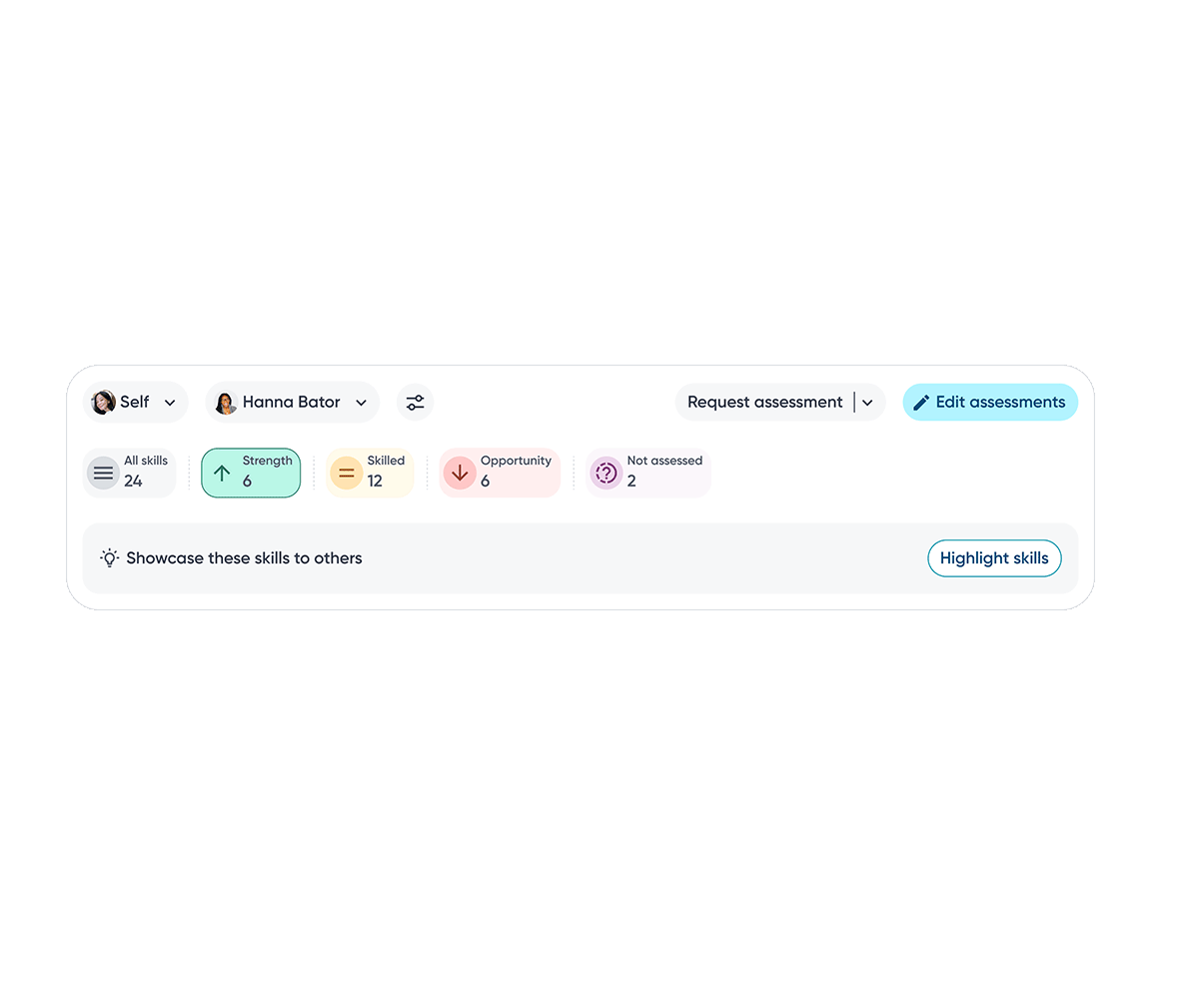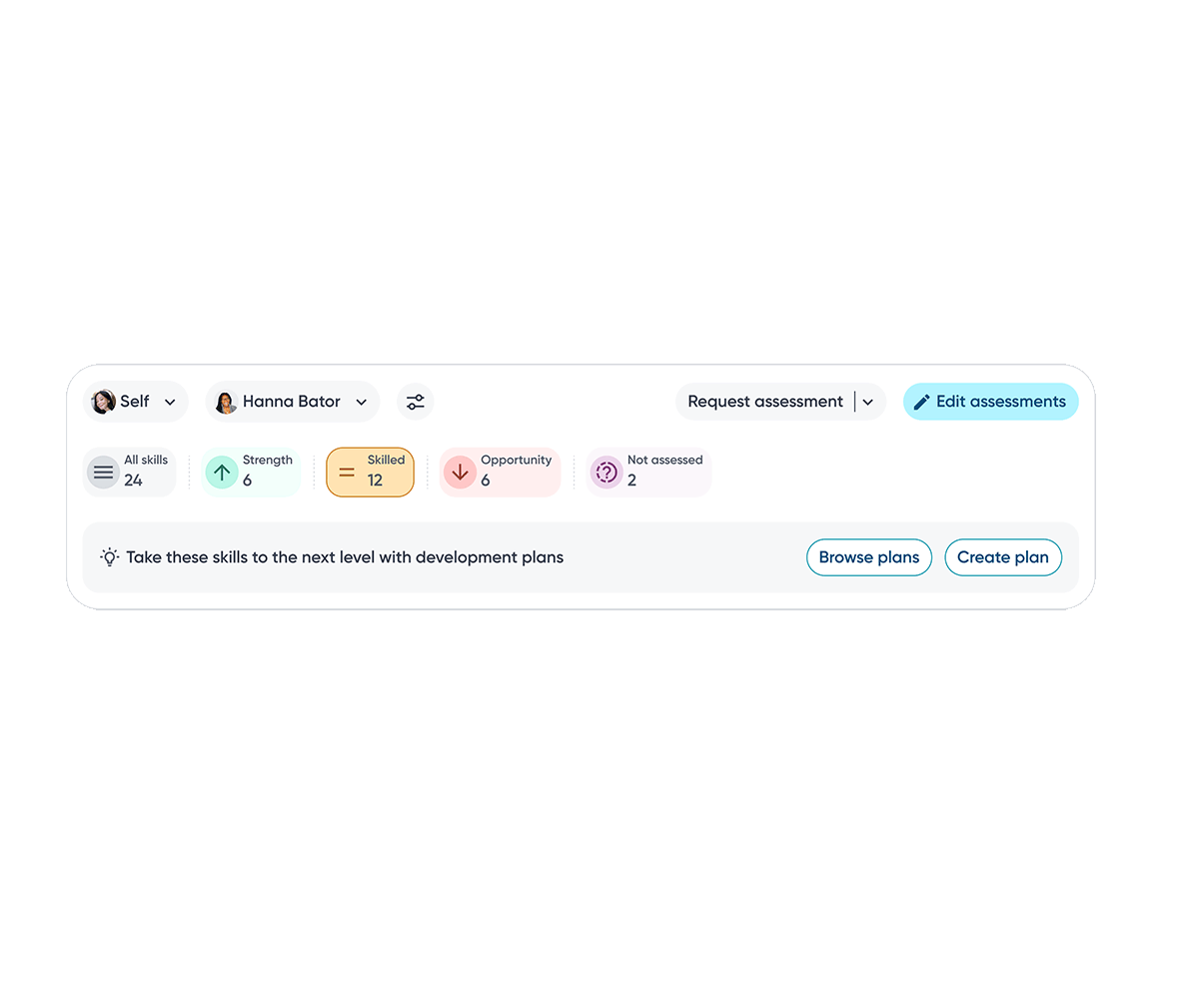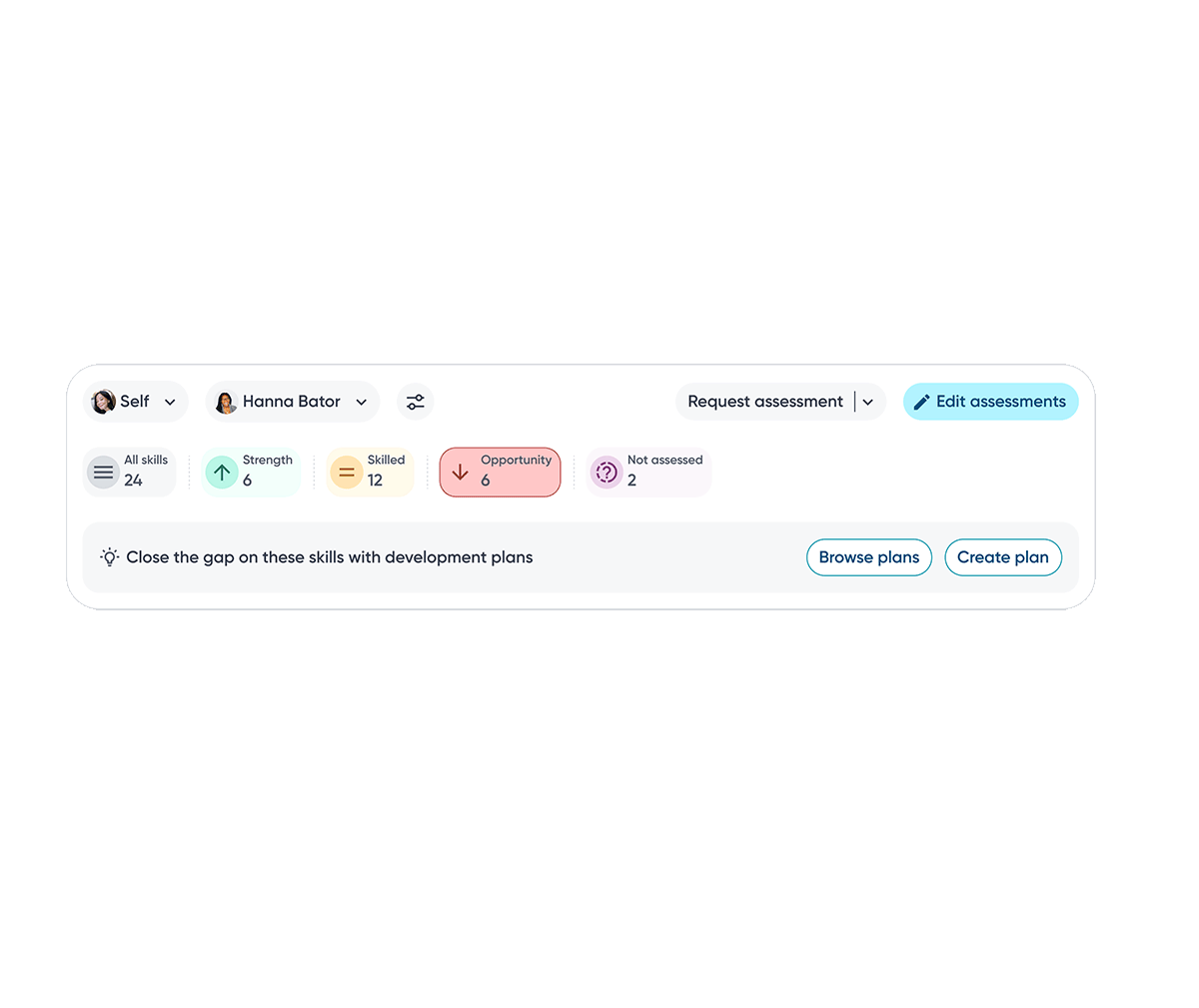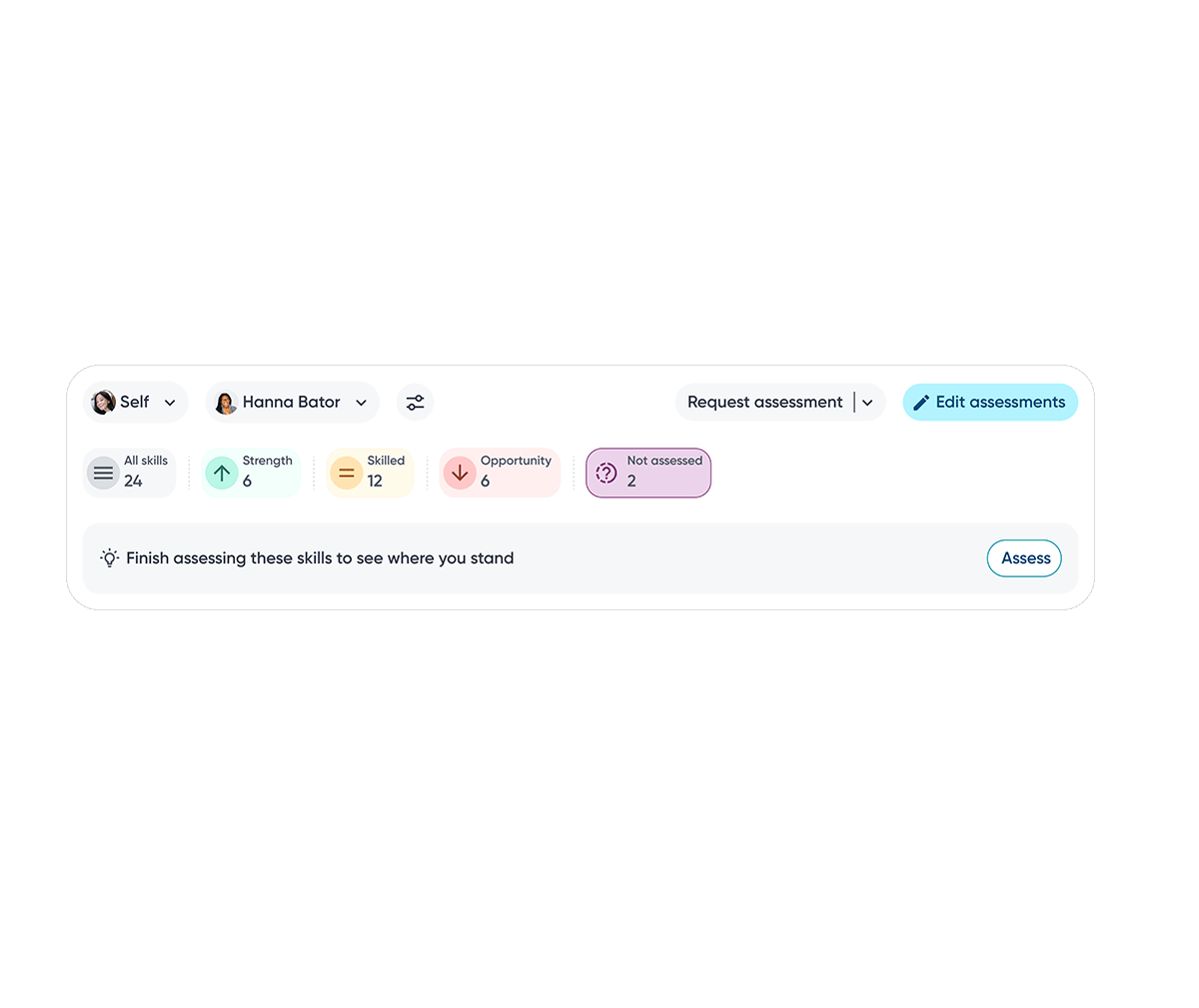
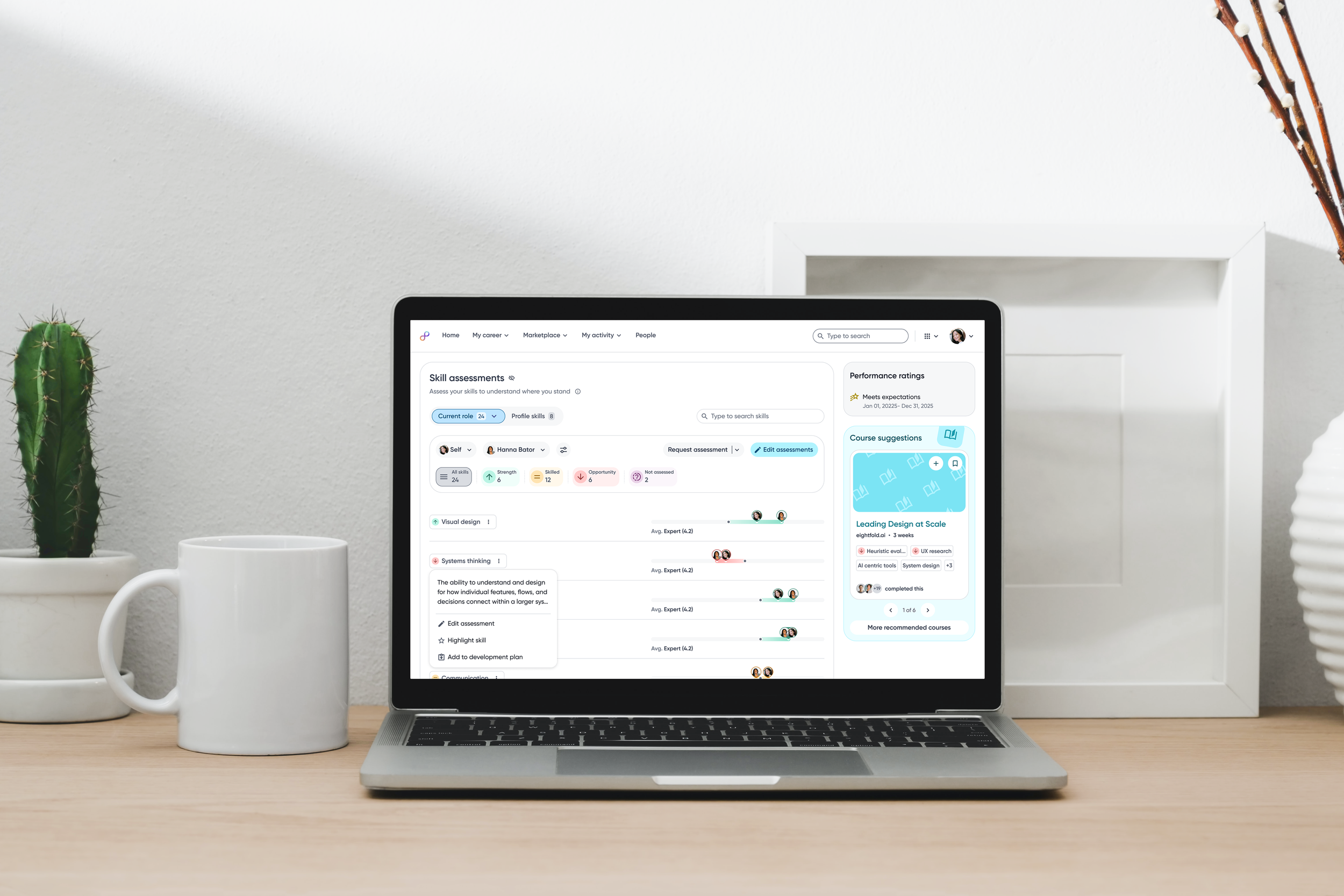
Icons are added to skill tags to clearly signal whether a skill is a strength, opportunity, or at the expected level, helping employees quickly understand their current proficiency.
Skill descriptions provide immediate clarity and shared context.
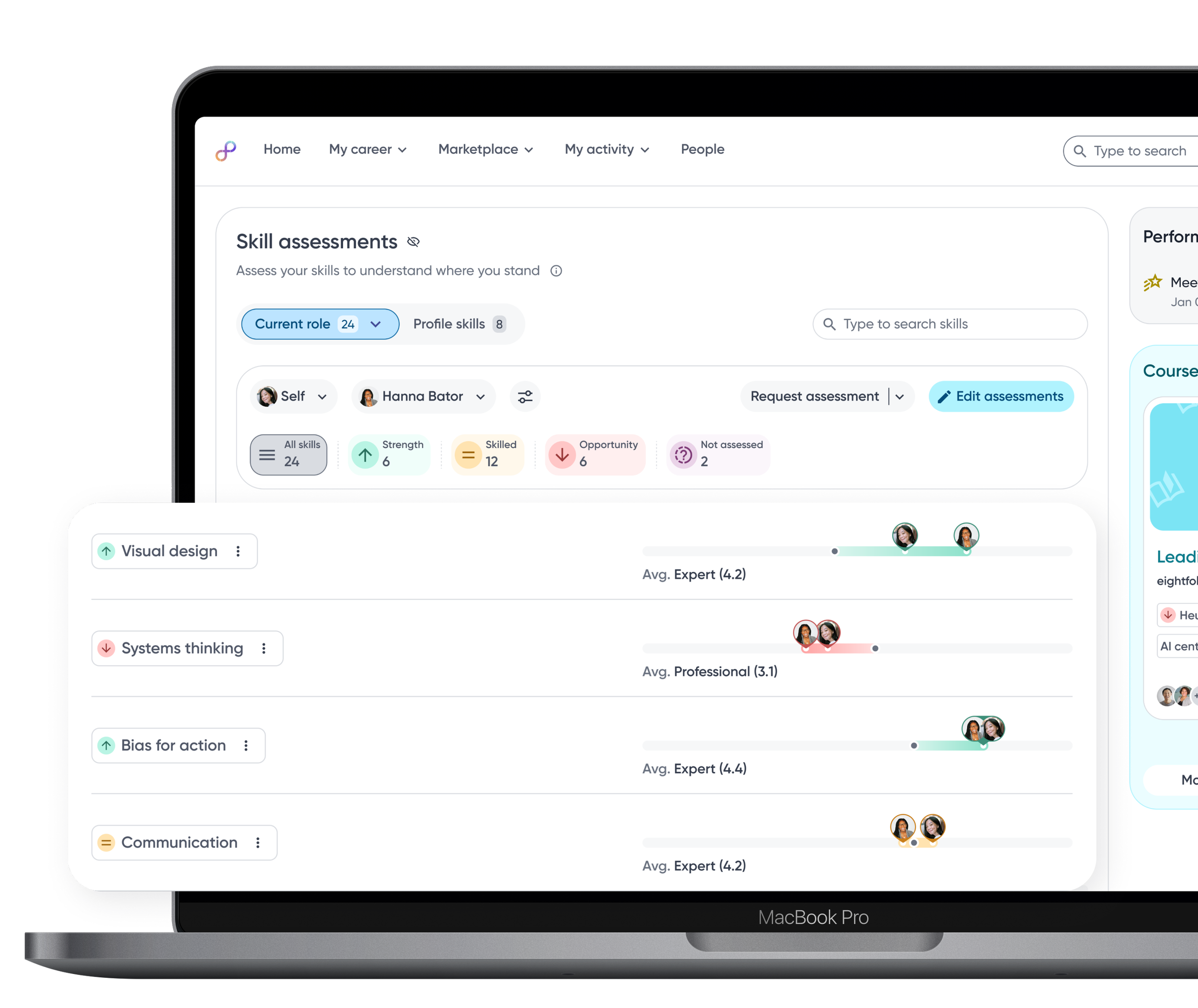
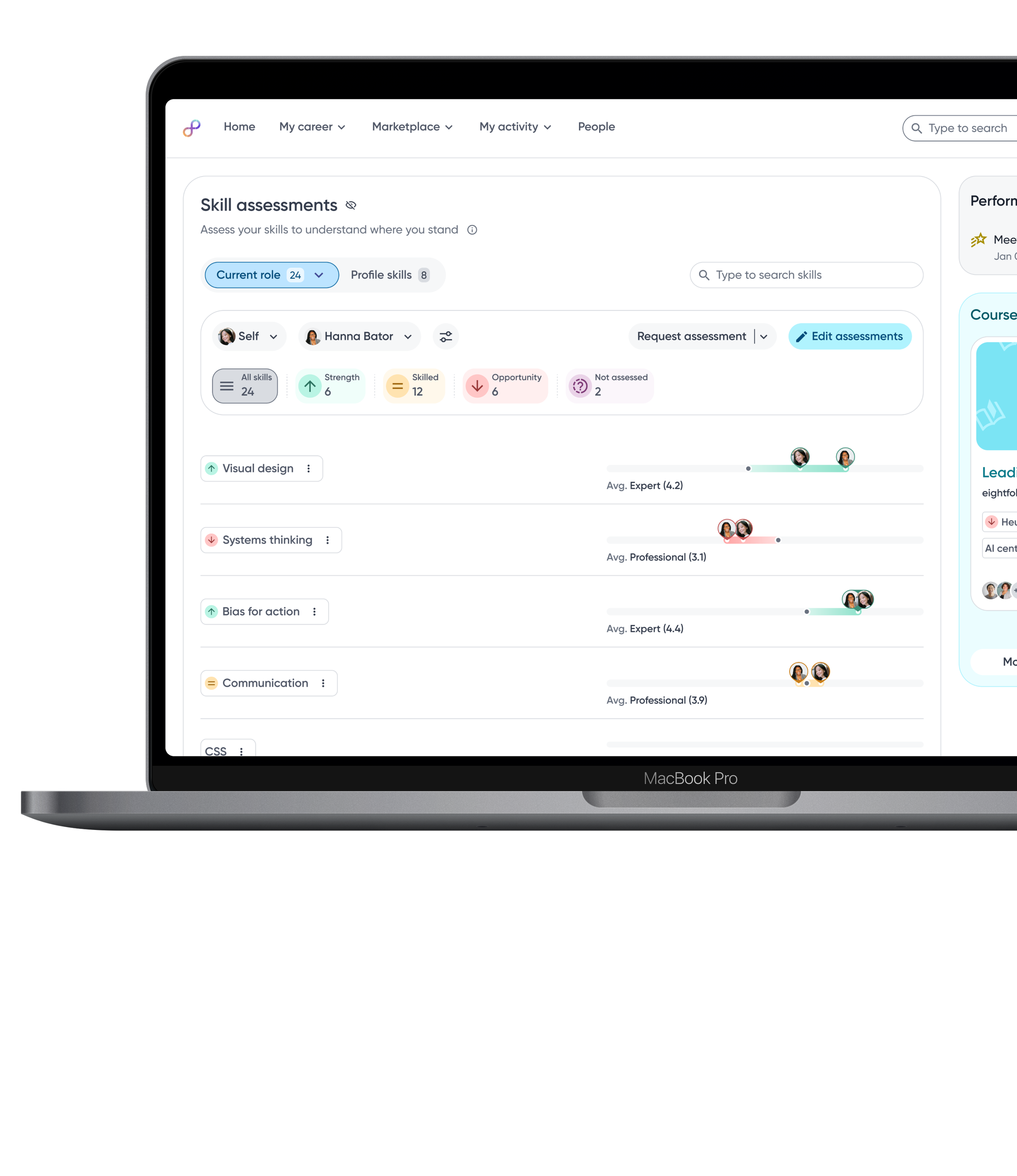
Raw skill assessment data is visualized as relative bars, enabling employees to quickly compare their proficiency against role benchmarks and identify gaps at a glance.
Rich contextual skill menu
When users need more context or want to take action, the skill menu brings understanding and next steps together, putting clarity, control and decision making in one place.
Contextual actions allow employees to edit, highlight or add skills to plans to development plans.
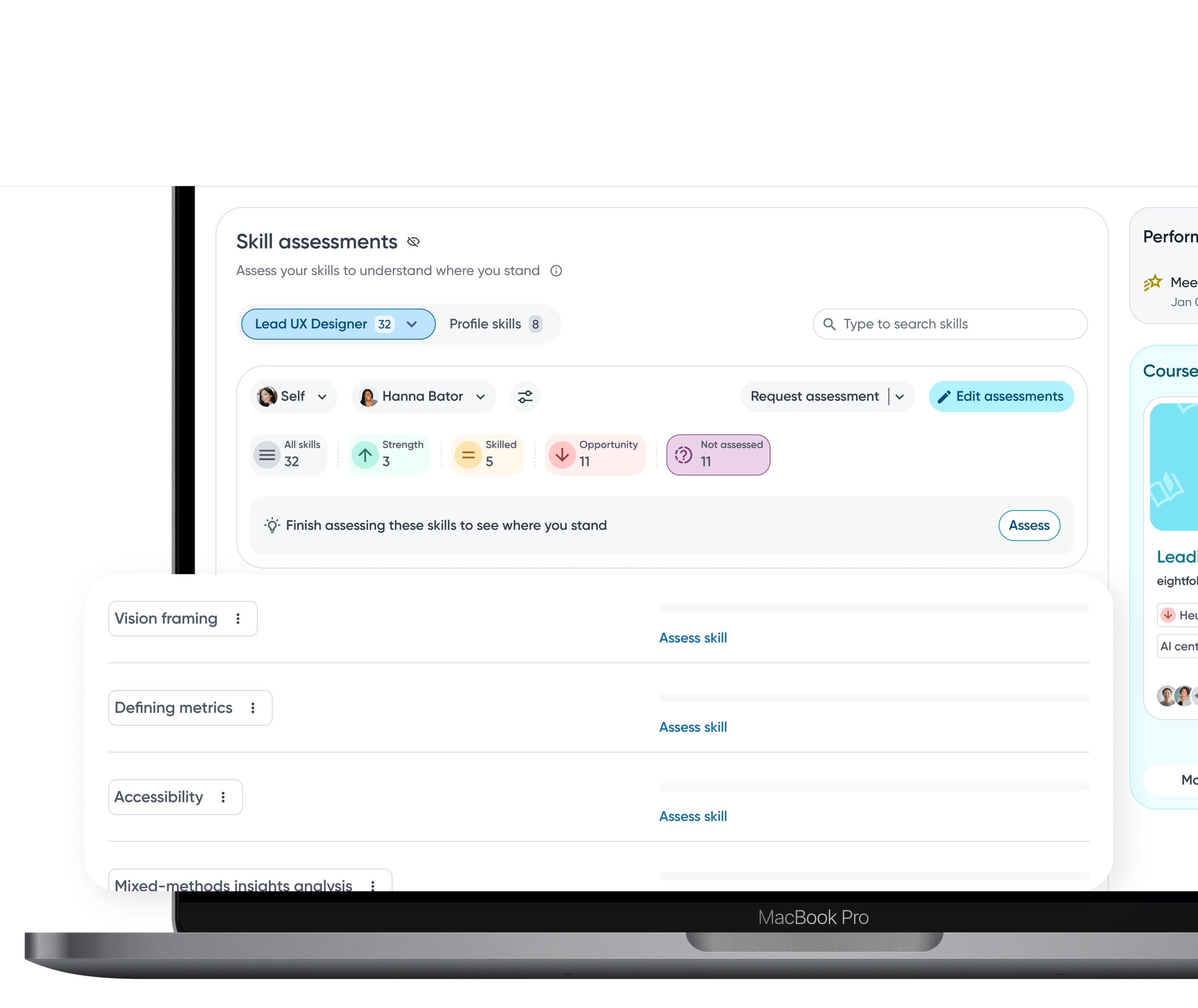
Assessment details
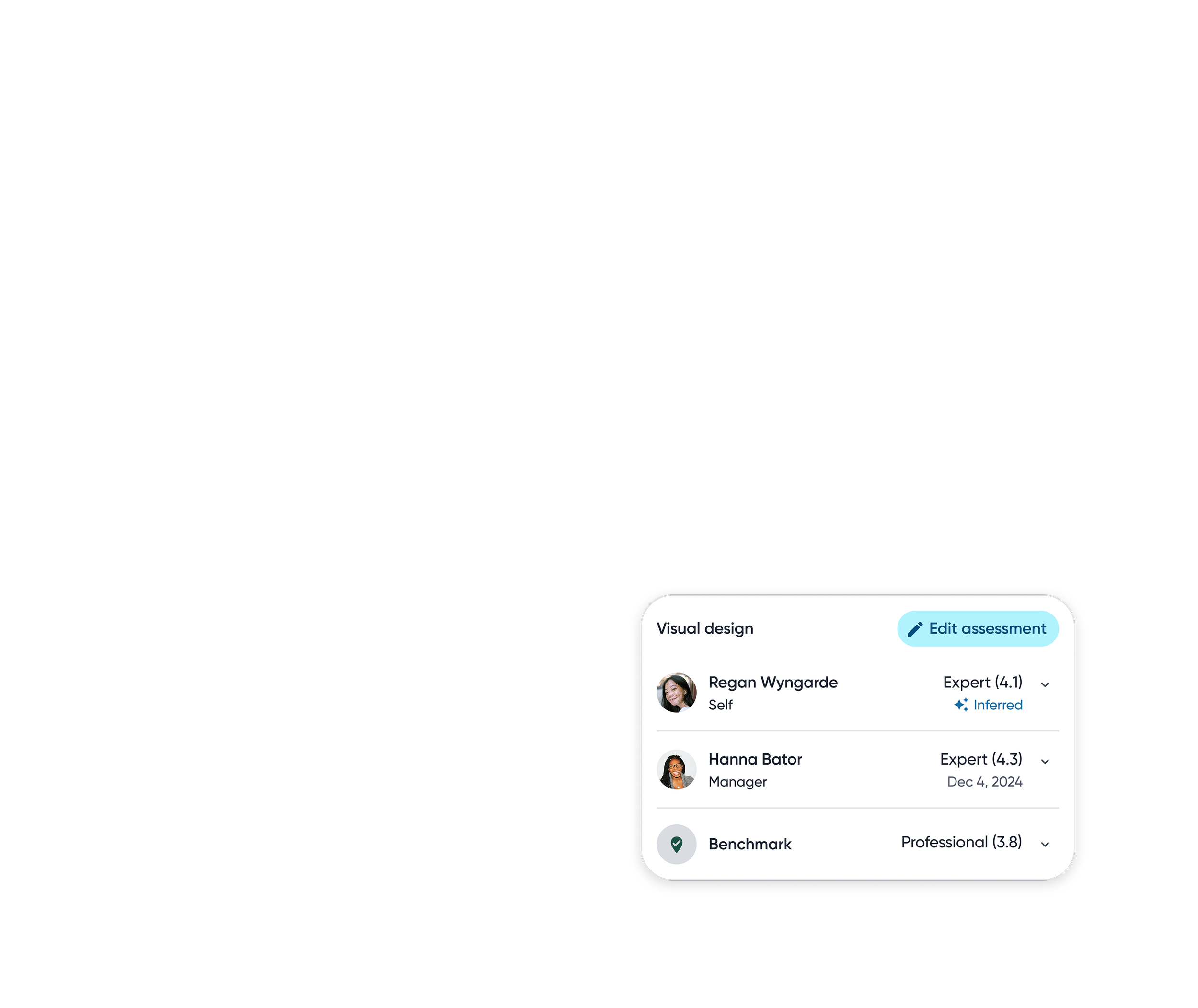
To support deeper understanding, the ratings popover reveals detailed numeric scores along clear descriptions for each proficiency level.
Granular visibility into skill ratings across different inputs.
Skill proficiency can be inferred with AI from rich, real world signals captured across the employee’s work
ALIGNING
Get a second, third, fourth… opinion
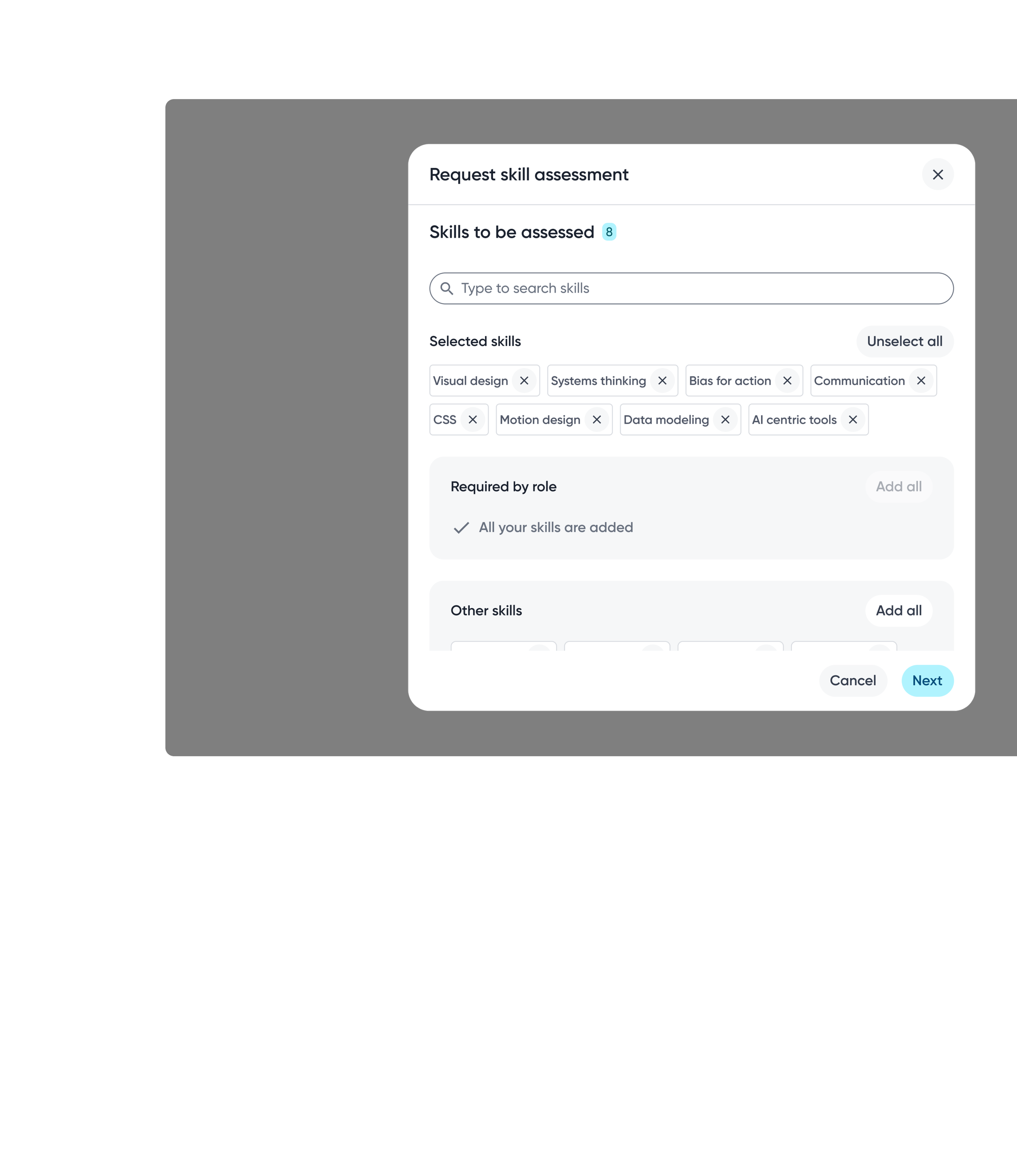
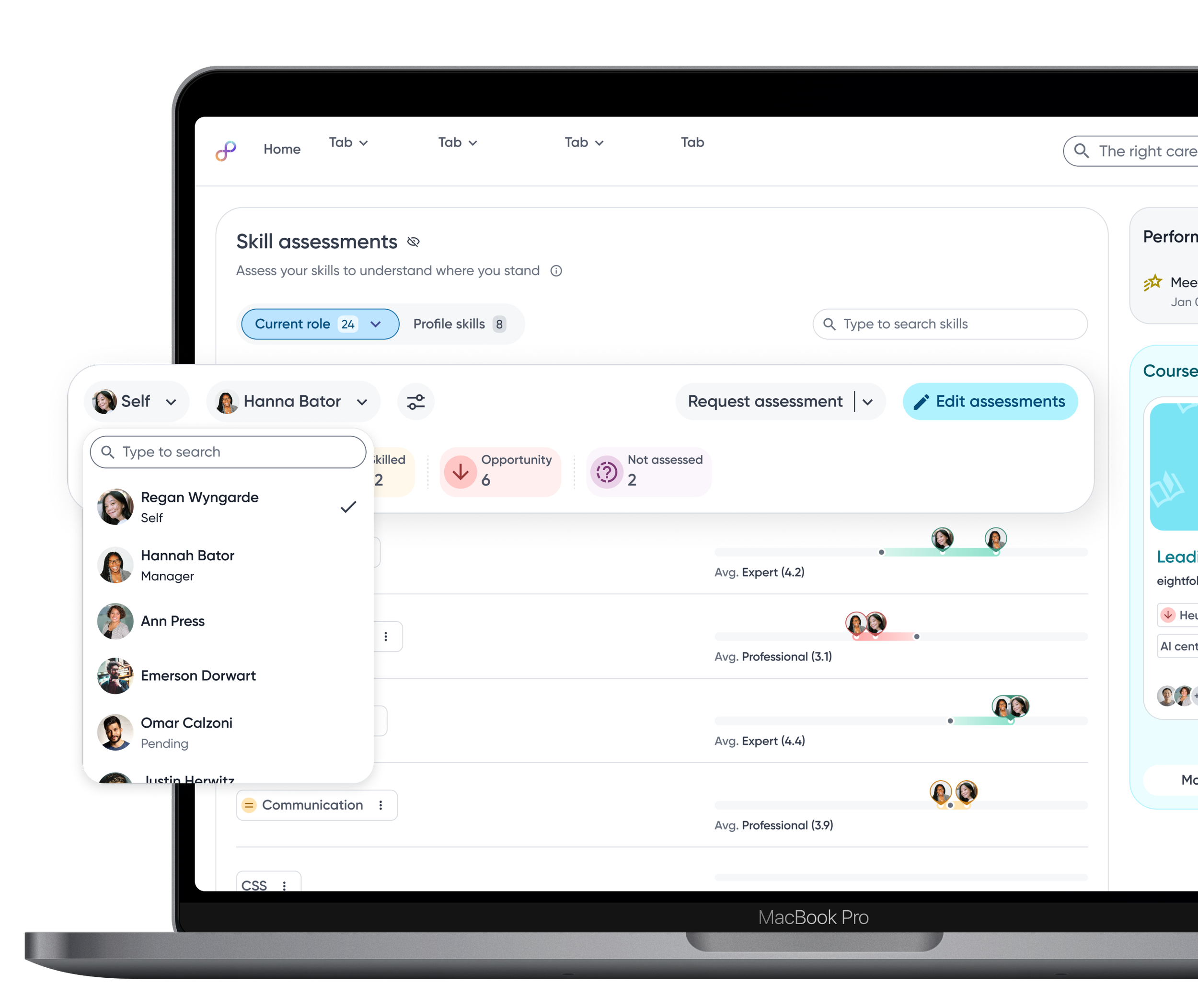
Skills are shaped through collaboration. Supporting peer assessments and flexible assessor selection allows skill data to capture diverse perspectives and reflect how skills are experienced in real work.
Peer assessment request
🔍 RESEARCH FINDING
Peers were seen as the must trusted signal for day-to-day skills. Feedback from colleagues who worked closely together was consistently perceived as more accurate and actionable.
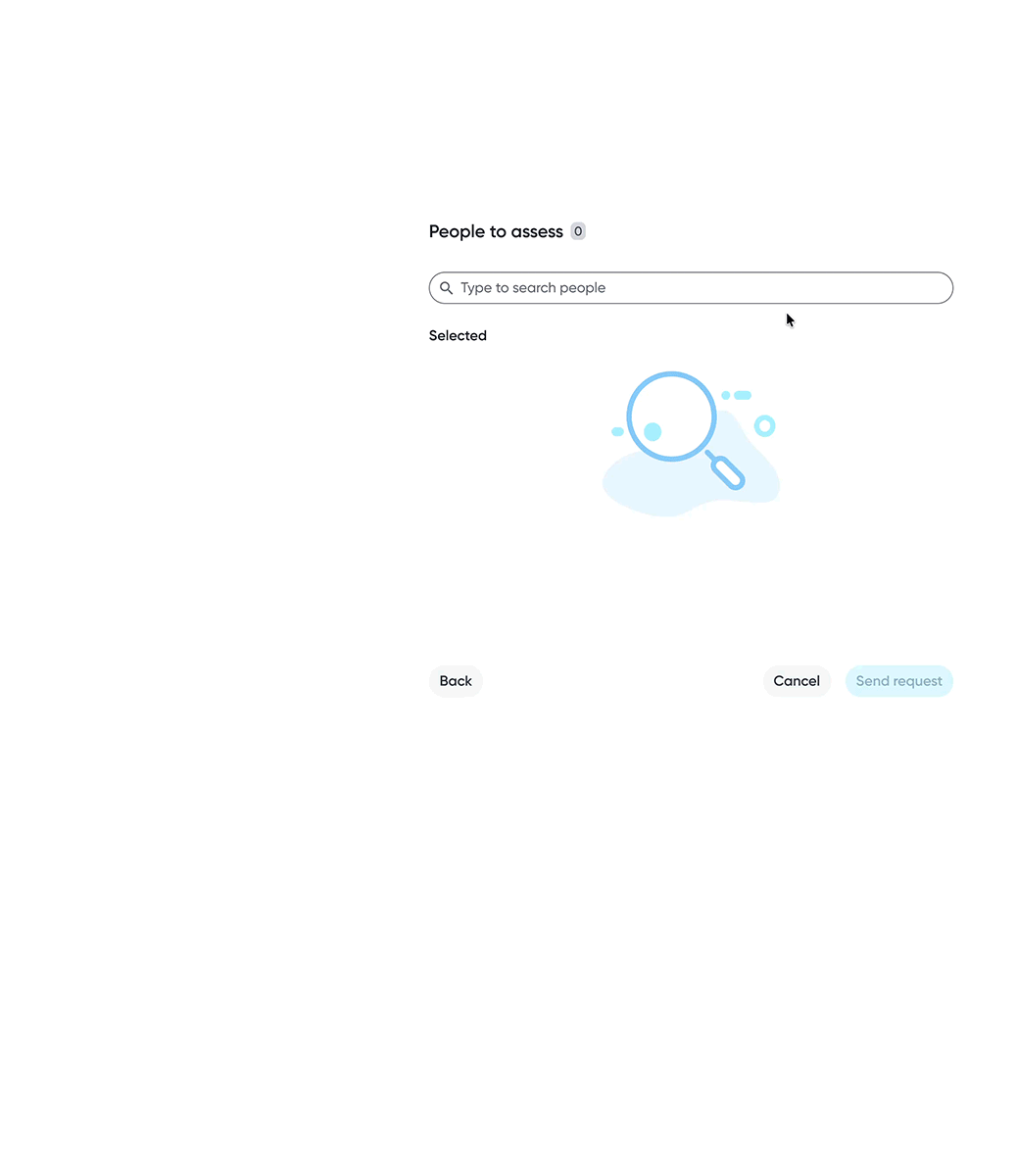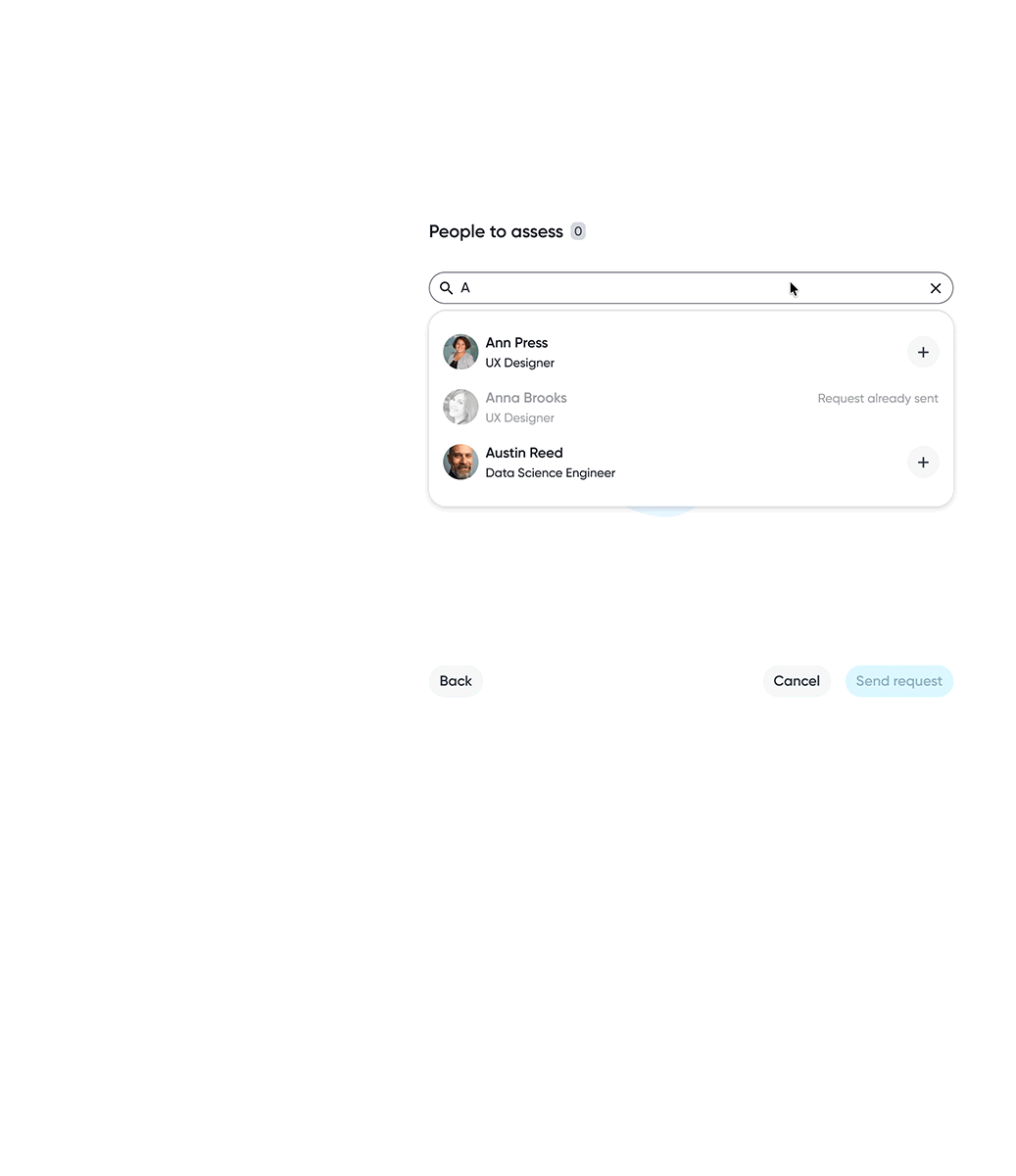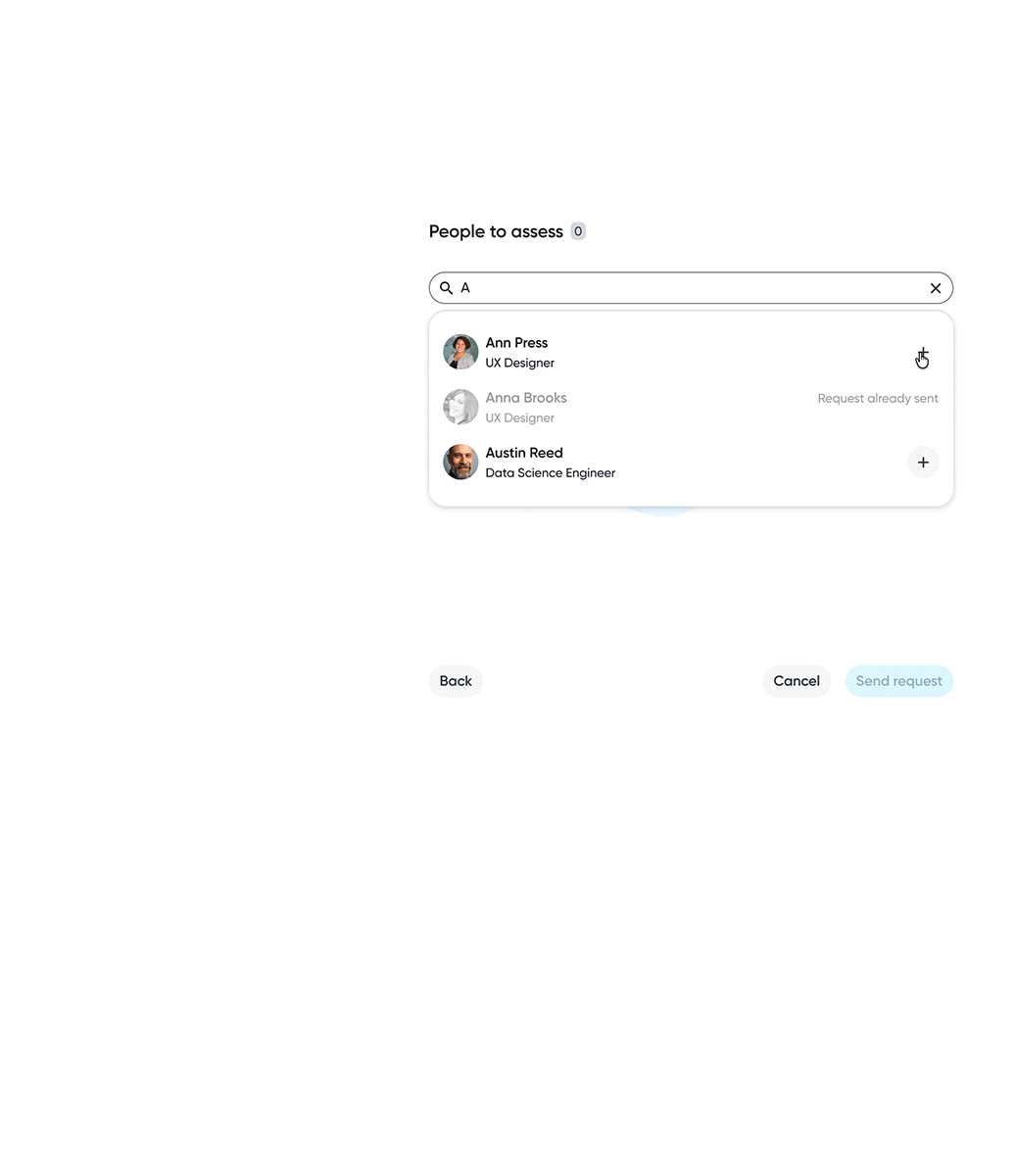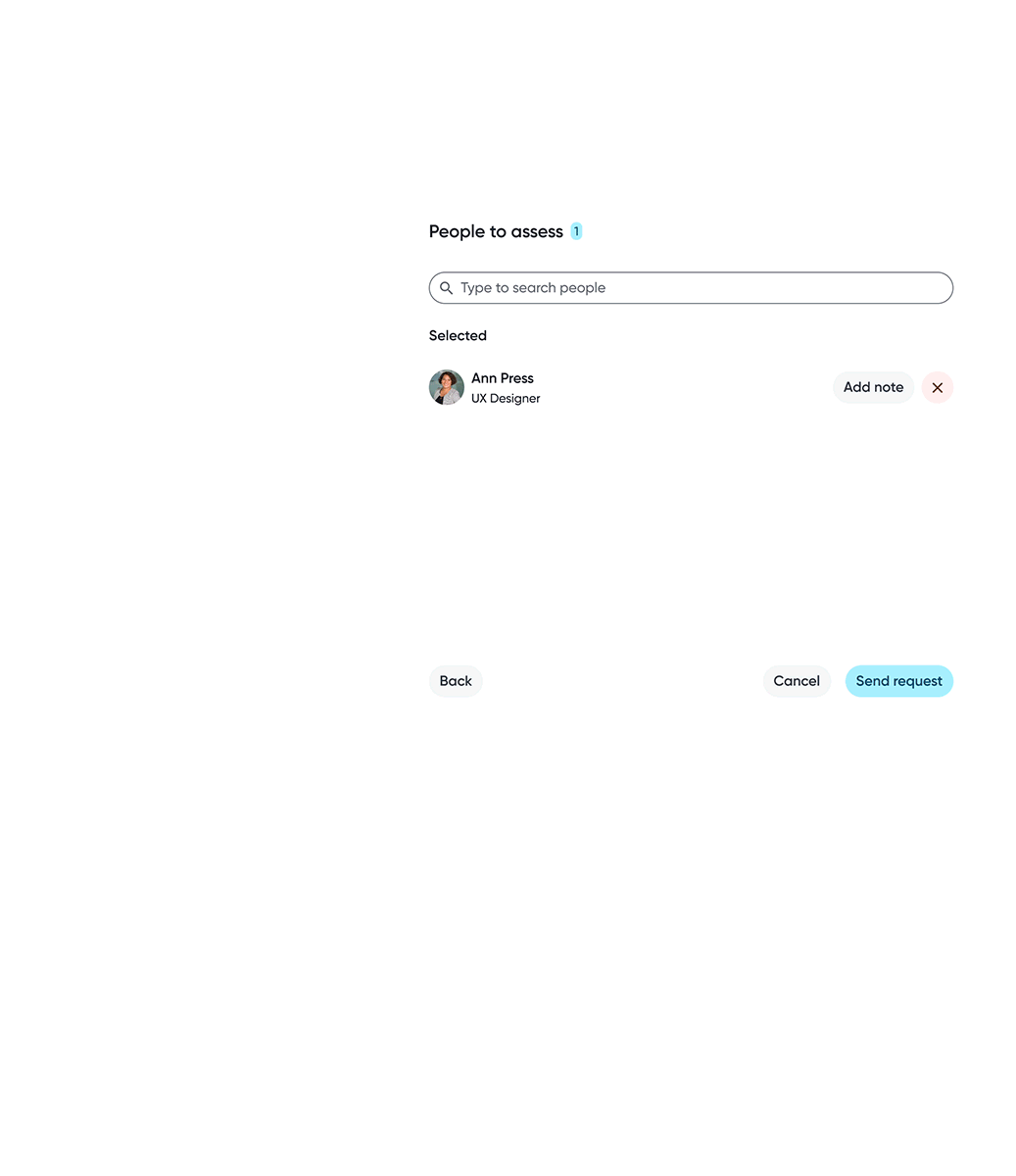
Assessor selection gives employees flexibility over which perspectives contribute to their skill data, supporting a more balanced assessment.
Employees can choose specific skills or include all skills when requesting assessments, depending on the level of feedback wanted.
It’s all about the details
The skill details panel consolidates everything related to a skill. From definition, assessments, endorsements, and goal history to give users a complete, contextual view in one place.
Contextual actions allow employees to move seamlessly from understanding a skill to taking meaningful next steps, keeping insight and momentum in the same place.
Assessment details provide transparent, multi-perspective view of how the skill is perceived, helping users build trust in the data and understand nuance across feedback.
Endorsements add qualitative context and social proof, reinforcing credibility and showing how skills are recognized and valued in real work.
ACTING
Making Skill Data Actionable
For skill data to create real impact, insight must translate into action. Making skill data actionable means surfacing the right next steps at the moment of awareness—so users can move seamlessly from understanding gaps to taking meaningful action.
Actions bar
🔍 RESEARCH FINDING
Long, undifferentiated lists of skills make it difficult for employees to identify priorities, limiting their ability to act on what matters most even when ratings are available.
Relevant actions are surfaced contextually within each skill category, enabling employees to proactively take steps towards skills development.
Create or browse development plans and add skills to improve.
Skills are grouped into gap categories such as strengths and opportunity so employees can quickly focus on areas that need attention.
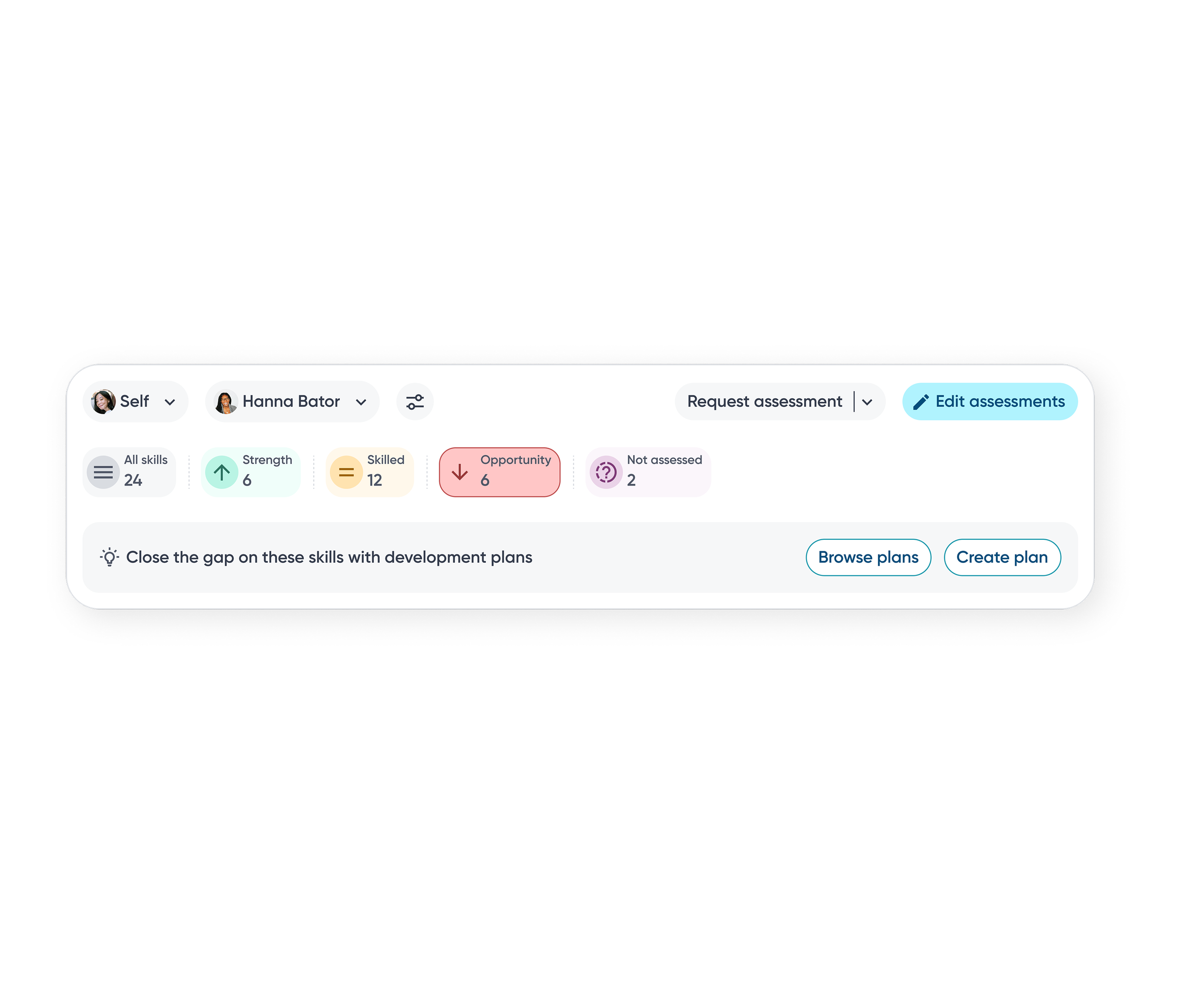
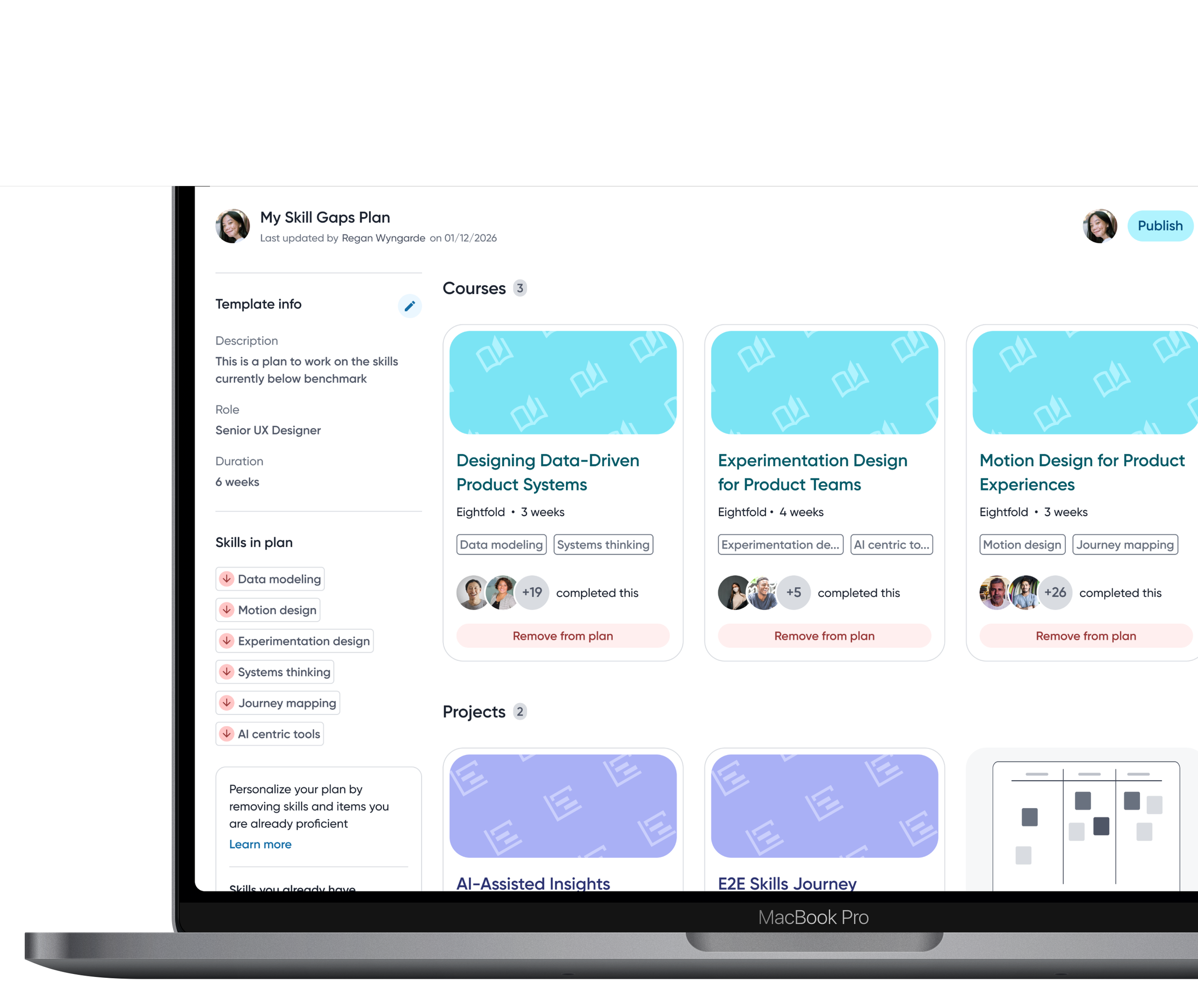
Close the gap
Employees can close the loop on skill gaps by adding them directly into development plans and receiving recommended courses or projects to close the gap.
Selecting assessors
Employees can switch between assessors to view skill proficiency from multiple perspectives, helping them understand context, differences, and potential blind spots.
GROWING
Making Skill Data Actionable for Career Growth
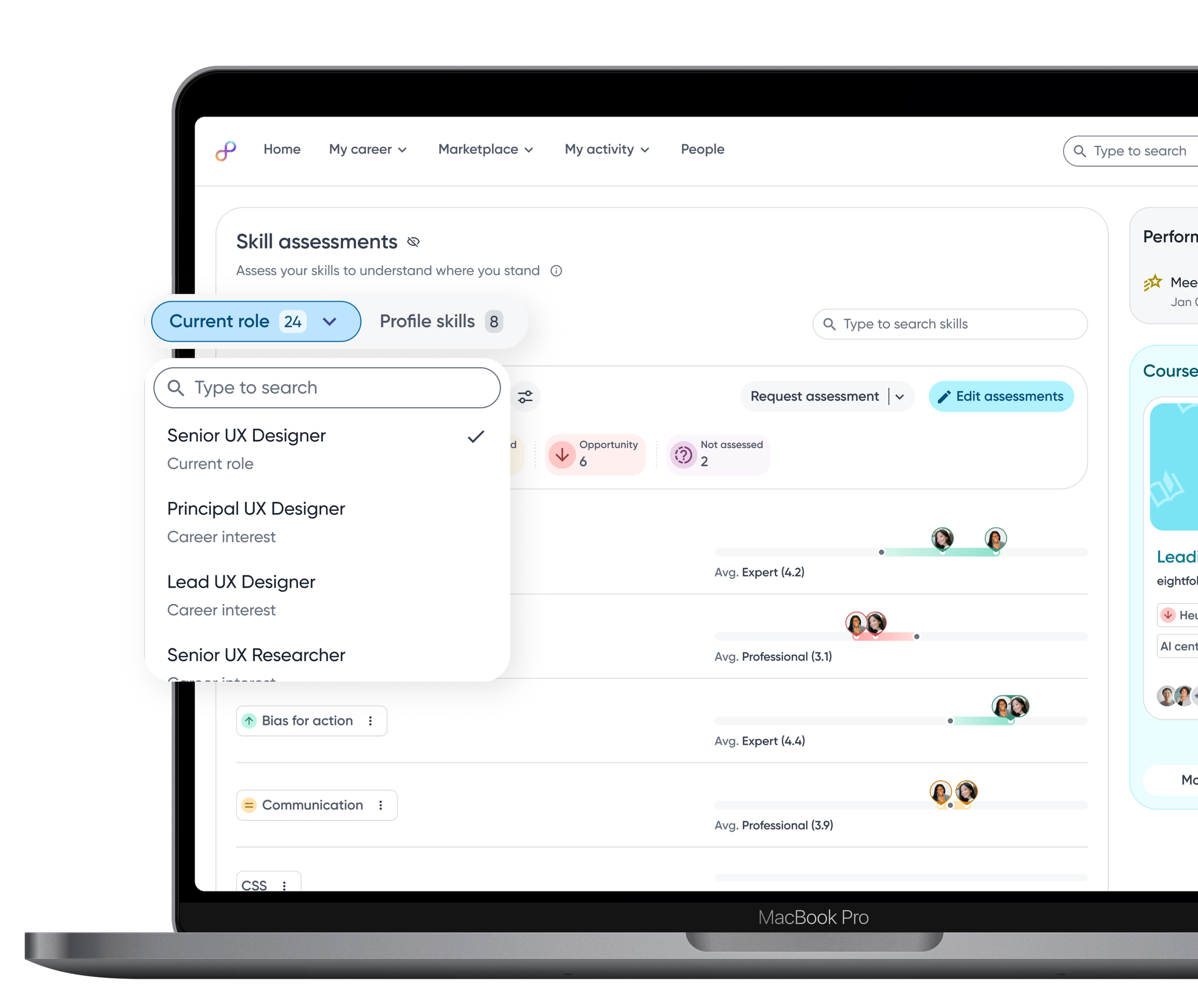
Skill data becomes even more powerful when it supports what’s next. Comparing proficiency against role benchmarks helps employees gauge readiness and target growth toward future roles.
🔍 RESEARCH FINDING
Employees viewed skills as a career signal, not just a performance metric. Many employees wanted to understand how their current skills translated to future roles, not just how they performed in their current one.
Skills to grow into
Seeing which skills are missing for a desired role helps employees understand what to learn next and removes guesswork from career growth.
Plan for missing skills
Contextual actions guide employees to set skills as goals or add them directly to development plans, helping them prepare for target roles.
MANAGER • TEAM INSIGHTS
Turning Team Skills into Action
Managers don’t just need visibility into team skills, they need clarity on where to focus and what to do next. This experience surfaces team-level skill gaps, strengths, and team insights in a way that supports proactive decision-making, helping managers address risks early and guide development with confidence.
CONTEXTUALIZING
Making Skill Data Work for Teams
Managing skills is complex at every level, from people managers to directors. Manager insights simplify this complexity by highlighting what matters most and guiding timely, confident action.
🔍 RESEARCH FINDING
Managers across roles rely on manual, fragmented tools to track team skills, making it difficult to prioritize, act, and defend decisions. There is a strong need for a centralized, skills-first view that surfaces team health at a glance, supports drill-down when needed, and pairs insight with clear next actions. Lightweight, explainable metrics augmented by AI recommendations and supporting evidence help managers move faster, stay fair, and address skill gaps proactively.
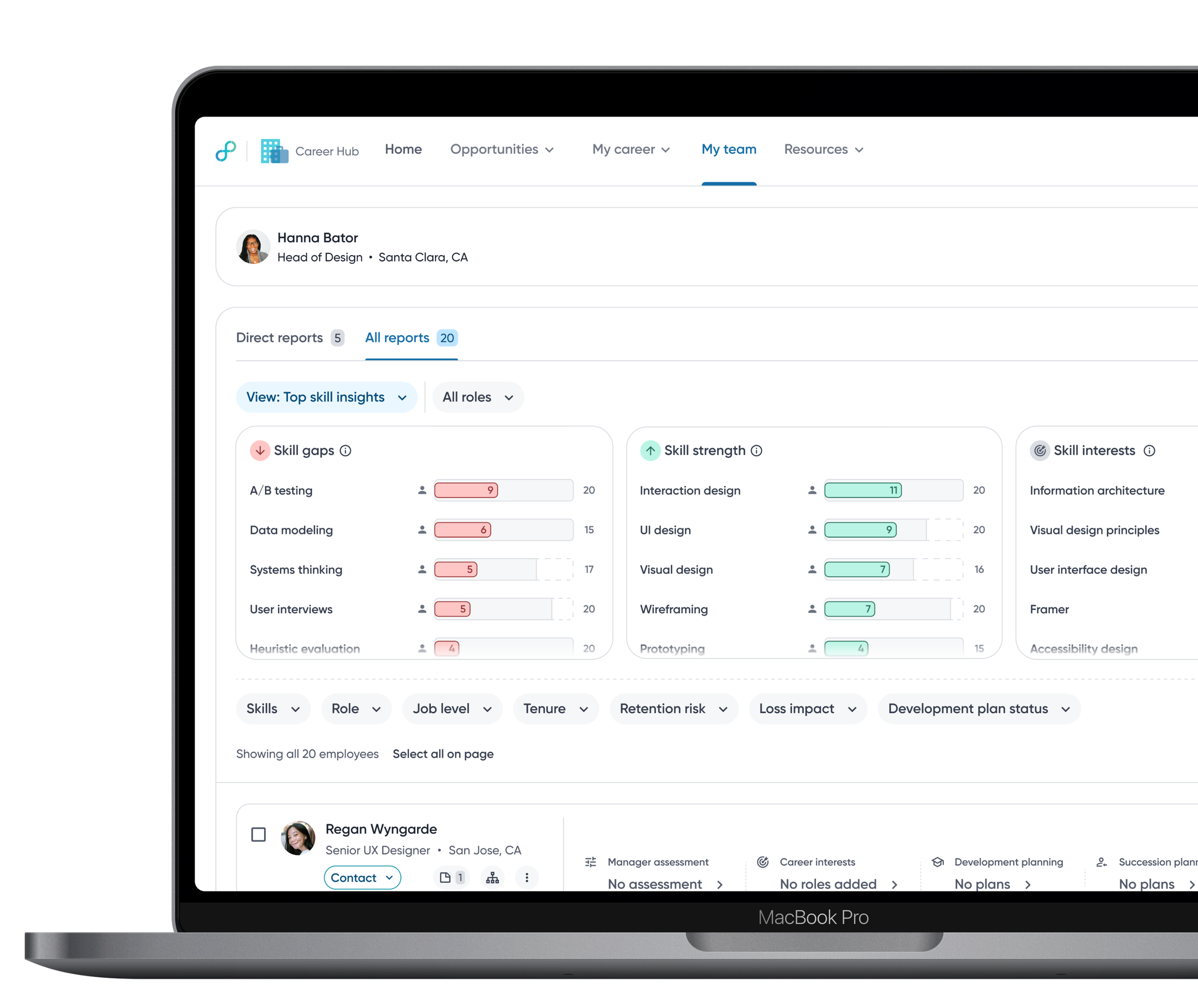
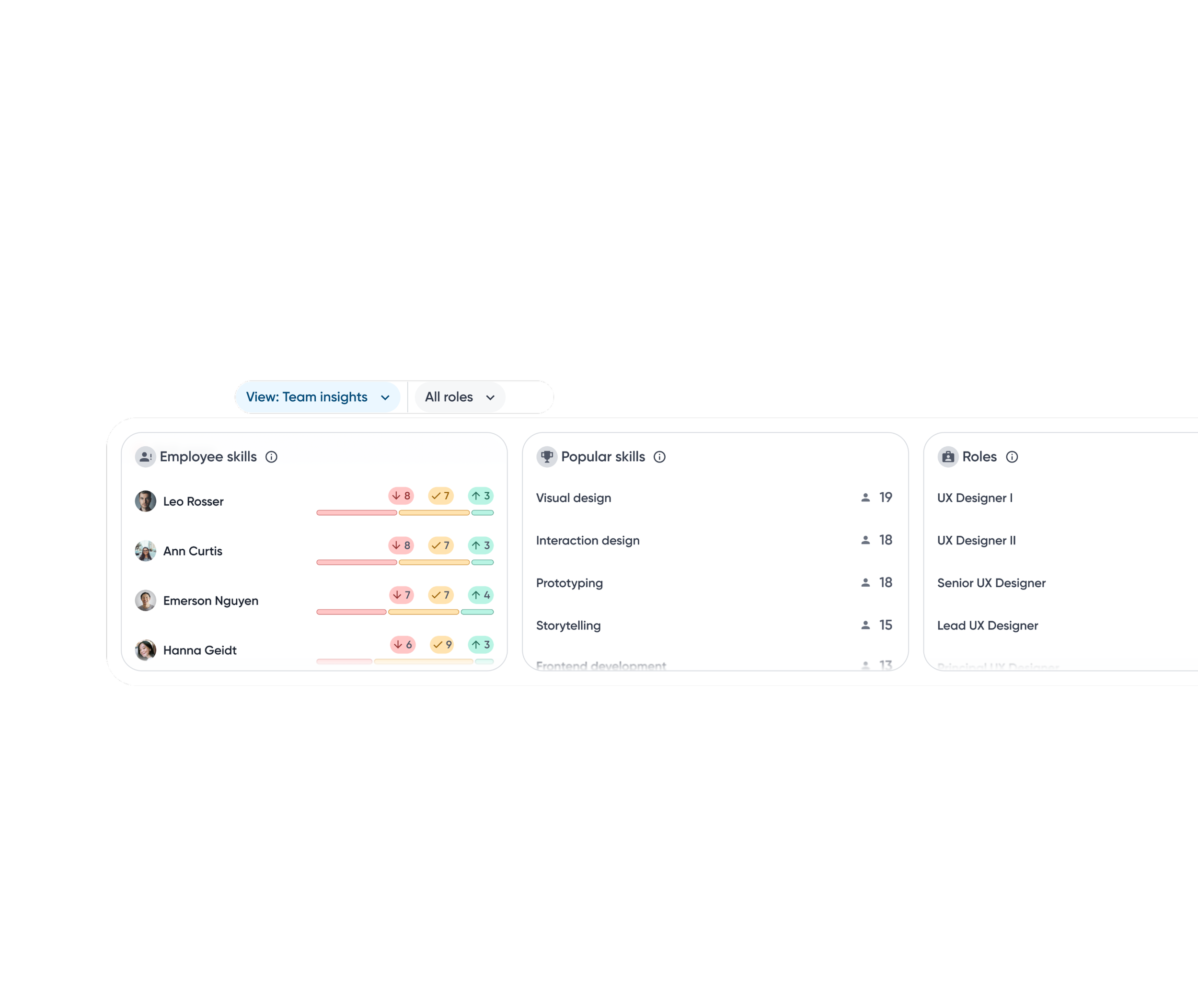
Grouping insights
Skill insight modules are grouped by related signals to help managers move from understanding overall team health to exploring individual details.
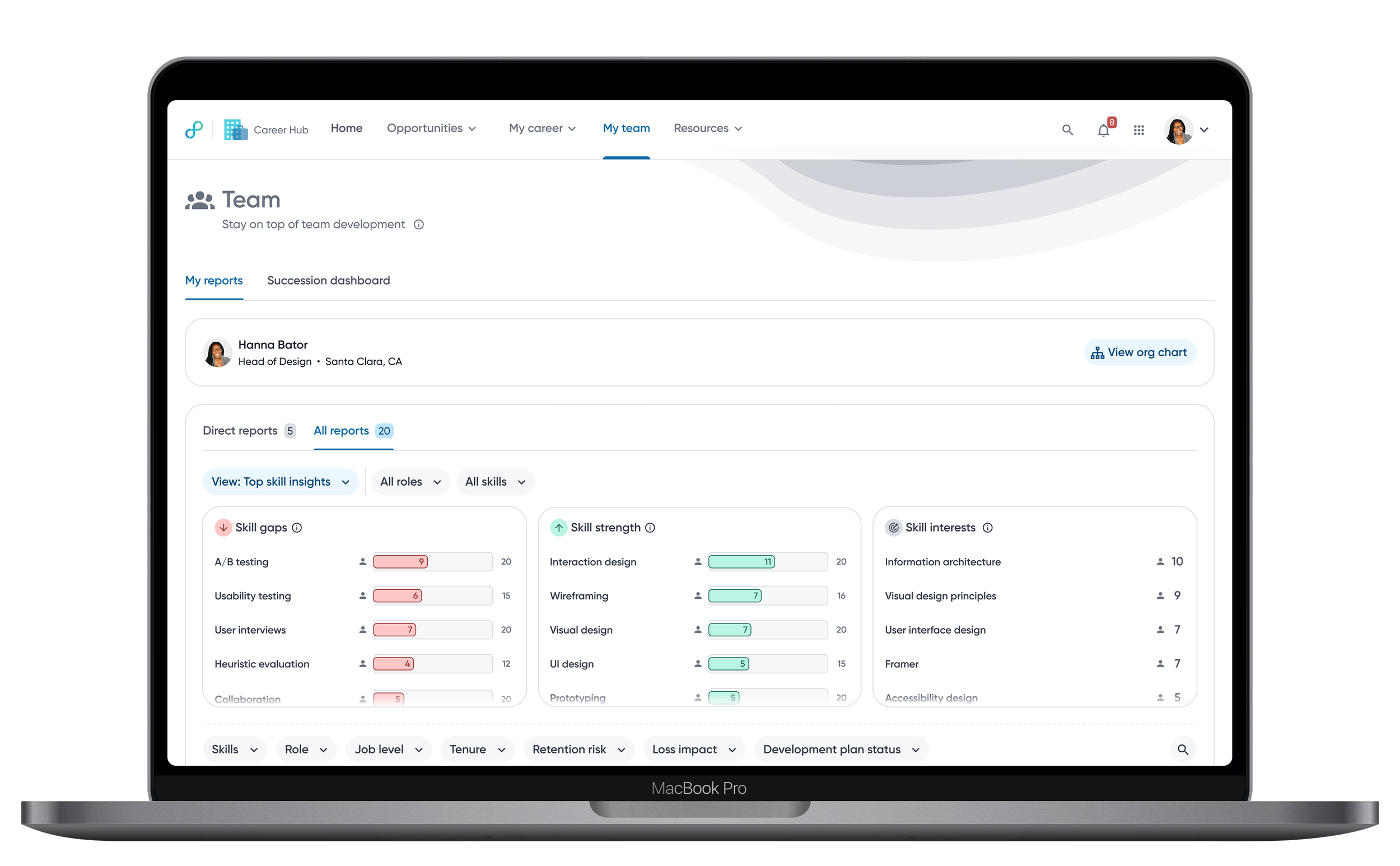
Top skill insights
A snapshot of where gaps exist, where the team is strong, and where growth is headed.
Bar chart visualizes how many employees fall above or below benchmarks relative to role expectations, making impact immediately visible.
A base track highlights employees without assessment data, indicating potential hidden gaps due to missing data.
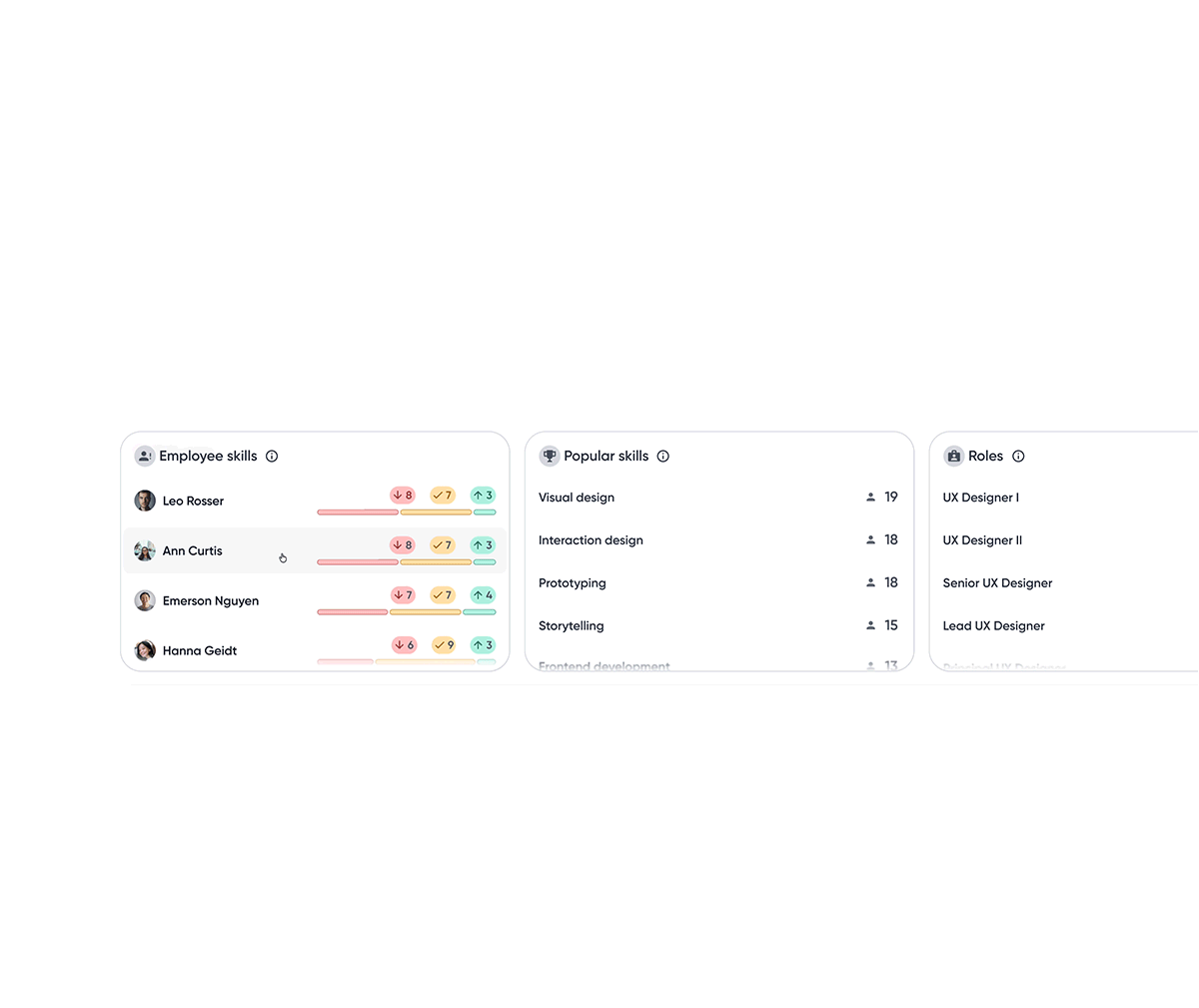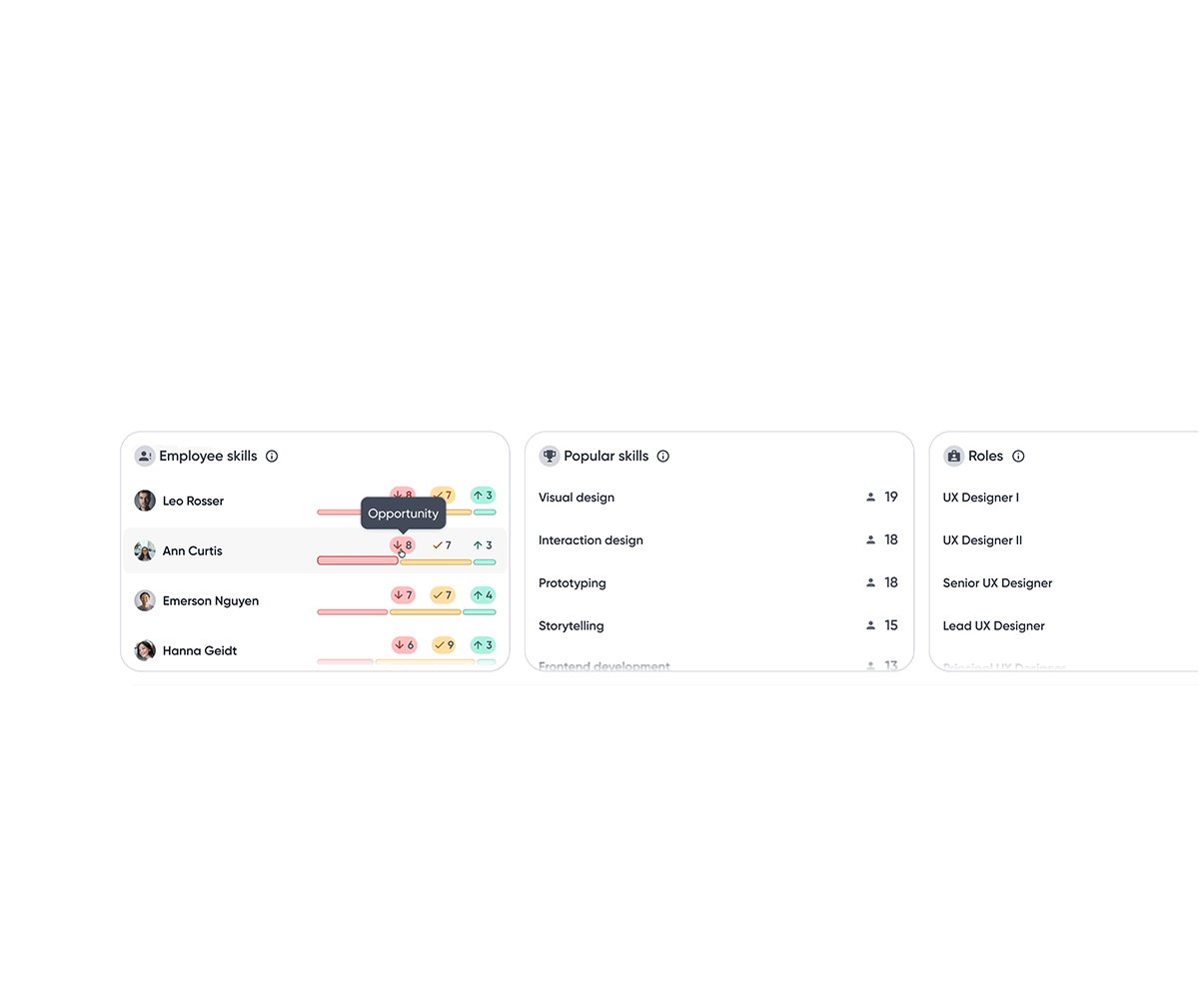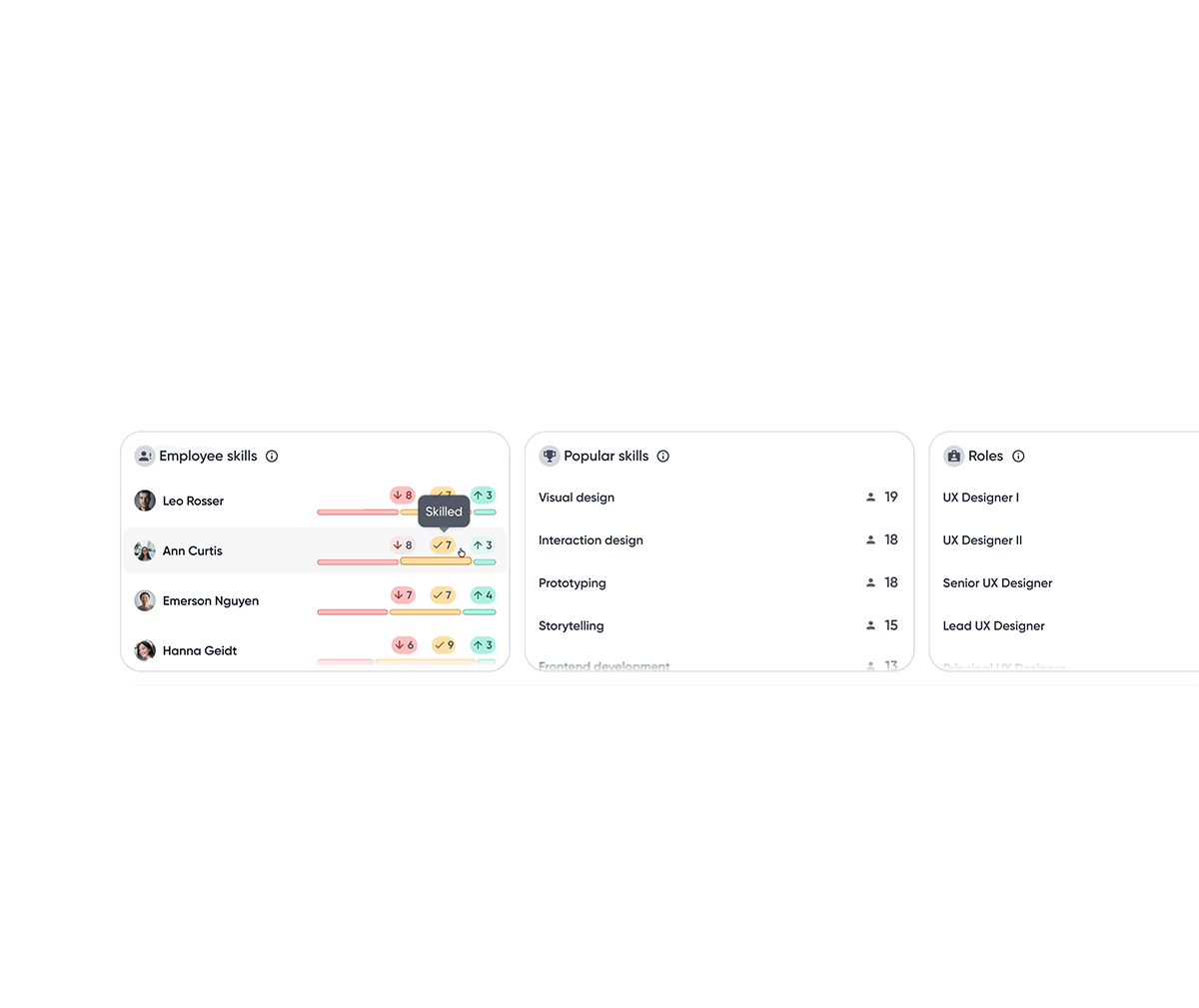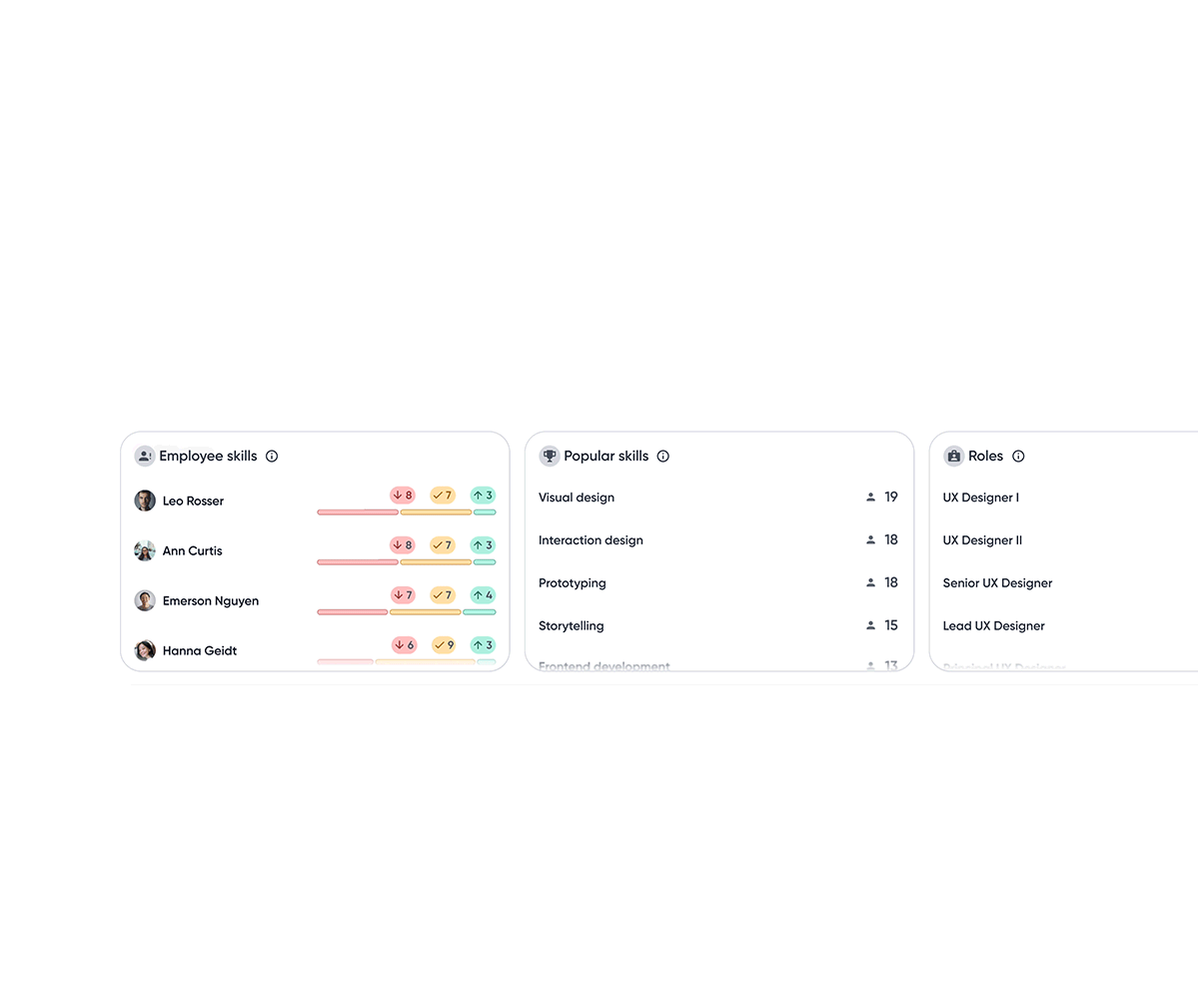
Employee skills module sorts employees with the most skill gaps, helping managers identify who needs attention most.
Insights are sorted by percentage to account for uneven skill coverage across roles, making gaps and strengths easier to compare.
Clicking an insight filters the employee list, enabling quick drill-down from team signals to individuals.
Team insights
A snapshot highlighting employees with the largest skill gaps along with skills most prevalent across the team.
Popular skills surface widely held skills, allowing managers to better plan staffing and allocate resources.